CT radiomics nomogram predicts pathological response after induced chemotherapy and overall survival in patients with advanced laryngeal cancer: A single-center retrospective study
- PMID: 37064100
- PMCID: PMC10103838
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1094768
CT radiomics nomogram predicts pathological response after induced chemotherapy and overall survival in patients with advanced laryngeal cancer: A single-center retrospective study
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to develop a radiomics nomogram to predict pathological response (PR) after induction chemotherapy (IC) and overall survival (OS) in patients with advanced laryngeal cancer (LC).
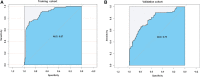
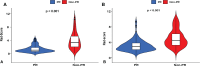
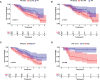
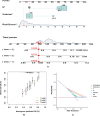
Methods: This retrospective study included patients with LC (n = 114) who had undergone contrast computerized tomography (CT); patients were randomly assigned to training (n = 81) and validation cohorts (n = 33). Potential radiomics scores were calculated to establish a model for predicting the PR status using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression. Multivariable logistic regression analyses were performed to select significant variables for predicting PR status. Kaplan-Meier analysis was performed to assess the risk stratification ability of PR and radiomics score (rad-score) for predicting OS. A prognostic nomogram was developed by integrating radiomics features and clinicopathological characteristics using multivariate Cox regression. All LC patients were stratified as low- and high-risk by the median CT radiomic score, C-index, calibration curve. Additionally, decision curve analysis (DCA) of the nomogram was performed to test model performance and clinical usefulness.
Results: Overall, PR rates were 45.6% (37/81) and 39.3% (13/33) in the training and validation cohorts, respectively. Eight features were optimally selected to build a rad-score model, which was significantly associated with PR and OS. The median OS in the PR group was significantly shorter than that in the non-PR group in both cohorts. Multivariate Cox analysis revealed that volume [hazard ratio, (HR) = 1.43], N stage (HR = 1.46), and rad-score (HR = 2.65) were independent risk factors associated with OS. The above four variables were applied to develop a nomogram for predicting OS, and the DCAs indicated that the predictive performance of the nomogram was better than that of the clinical model.
Conclusion: For patients with advanced LC, CT radiomics score was an independent biomarker for estimating PR after IC. Moreover, the nomogram that incorporated radiomics features and clinicopathological factors performed better for individualized OS estimation.
Keywords: chemotherapy; laryngeal; nomogram; pathological response; radiomics.
Copyright © 2023 Kang, Sun, Yang, Zhang, Ning and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A CT-based deep learning radiomics nomogram for predicting the response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced gastric cancer: A multicenter cohort study.EClinicalMedicine. 2022 Mar 21;46:101348. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101348. eCollection 2022 Apr. EClinicalMedicine. 2022. PMID: 35340629 Free PMC article.
-
A prognostic nomogram for T3N0M0 esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients undergoing radical surgery based on computed tomography radiomics and inflammatory nutritional biomarkers.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Nov;25(11):e14504. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14504. Epub 2024 Sep 6. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 39241166 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Radiomics Nomogram Based on 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography and Clinicopathological Factors to Predict the Survival Outcomes of Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Jul 17;10:1042. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01042. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32766134 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a CT-based radiomics nomogram for predicting progression-free survival in patients with small cell lung cancer.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 May 6;25(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01691-4. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40329257 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Non-Invasive Radiomic Signature on CT Scans Predicts Response to Platinum-Based Chemotherapy and Is Prognostic of Overall Survival in Small Cell Lung Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 20;11:744724. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.744724. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34745966 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clinical application of CT-based radiomics model in differentiation between laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and squamous cell hyperplasia.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 11;10:1337723. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1337723. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38274455 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Forastiere AA, Ismaila N, Lewin JS, Nathan CA, Adelstein DJ, Eisbruch A, et al. . Use of larynx-preservation strategies in the treatment of laryngeal cancer: American society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol (2018) 36(11):1143–69. doi: 10.1200/jco.2017.75.7385 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Akbaba S, Held T, Lang K, Hoerner-Rieber J, Zaoui K, Forster T, et al. . Salvage radiotherapy for recurrent hypopharyngeal and laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (Scc) after first-line treatment with surgery alone: A 10-year single-centre experience. Radiat Oncol (2019) 14(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13014-019-1238-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Forastiere AA, Zhang Q, Weber RS, Maor MH, Goepfert H, Pajak TF, et al. . Long-term results of rtog 91-11: A comparison of three nonsurgical treatment strategies to preserve the larynx in patients with locally advanced larynx cancer. J Clin Oncol (2013) 31(7):845–52. doi: 10.1200/jco.2012.43.6097 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

