Case report: Primary pleural giant extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma in a child
- PMID: 37064103
- PMCID: PMC10102462
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1137586
Case report: Primary pleural giant extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma in a child
Abstract
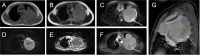
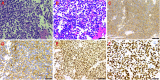
Primary extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma (EES) is a rare small round cell malignancy that accounts for less than 1% of all sarcomas. It is found most commonly in the trunk and lower limbs and very rarely in the pleura and can be easily misdiagnosed in clinical practice. This study presents the case of an 11-year-old boy who presented to our hospital with no apparent cause of left shoulder pain for 6 months. On physical examination, tenderness was noted in the left chest wall and shoulder joint, which had a limited range of motion. Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the chest revealed an irregular soft tissue mass in the upper left thorax, with a wide base attached to the adjacent pleura and bone destruction of the adjacent left first rib. The patient's bone scan showed a dense focus of increased radiotracer accumulation in the left first rib. A subsequent CT-guided aspiration biopsy of the left pleural mass with histomorphology and immunohistochemical phenotyping led to a diagnosis of extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma. To inhibit tumor growth, alternating systemic chemotherapy cycles of vincristine, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide (VDC) and isocyclophosphamide and etoposide (IE) were administered at 3-week intervals. After completing three VDC and two IE cycles, the child's condition was well and the pain in the left shoulder joint was relieved. However, a repeat MRI of the chest showed that the mass did not shrink.
Keywords: case report; computed tomography; extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma; intrathoracic tumor; malignancy.
Copyright © 2023 Wu, Xie, Huang and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Javery O, Krajewski K, Regan K, Kis B, Giardino A, Jagannathan J, et al. A to z of extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma family of tumors in adults: Imaging features of primary disease, metastatic patterns, and treatment responses. AJR. Am J Roentgenol (2011) 197:W1015–1022. doi: 10.2214/AJR.11.6667 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Somarouthu BS, Shinagare AB, Rosenthal MH, Tirumani H, Hornick JL, Ramaiya NH, et al. Multimodality imaging features, metastatic pattern and clinical outcome in adult extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma: Experience in 26 patients. Br J Radiol (2014) 87:20140123. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20140123 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huh J, Kim KW, Park SJ, Kim HJ, Lee JS, Ha HK, et al. Imaging features of primary tumors and metastatic patterns of the extraskeletal Ewing sarcoma family of tumors in adults: A 17-year experience at a single institution. Korean J Radiol (2015) 16:783–90. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.4.783 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

