Expression and molecular regulation of non-coding RNAs in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 37064141
- PMCID: PMC10090466
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1122982
Expression and molecular regulation of non-coding RNAs in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
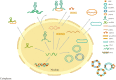
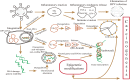
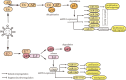
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is the sixth most prevalent malignancy worldwide. Accumulating evidence suggests that persistent HPV infection is closely related to a subset of HNSCC types, and the incidence of human papillomavirus (HPV)-positive HNSCC has been annually increasing in recent decades. Although the carcinogenesis of HPV-positive HNSCC has not been completely elucidated, it has been well confirmed that E6 and E7, the main viral oncoproteins are responsible for the maintenance of malignant transformation, promotion of cell proliferation, and increase in tumor invasion. Moreover, compared with HPV-negative HNSCC, HPV-positive HNSCC shows some special clinical-pathological features, which are possibly related to HPV infection and their specific regulatory mechanisms. Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is a class of RNA lacking the protein-coding function and playing a critical regulatory role via multiple complex molecular mechanisms. NcRNA is an important regulatory pattern of epigenetic modification, which can exert significant effects on HPV-induced tumorigenesis and progression by deregulating downstream genes. However, the knowledge of ncRNAs is still limited, hence, a better understanding of ncRNAs could provide some insights for exploring the carcinogenesis mechanism and identifying valuable biomarkers in HPV-positive HNSCC. Therefore, in this review, we mainly focused on the expression profile of ncRNAs (including lncRNA, miRNA, and circRNA) and explored their regulatory role in HPV-positive HNSCC, aiming to clarify the regulatory mechanism of ncRNAs and identify valuable biomarkers for HPV-positive HNSCC.
Keywords: circular RNAs; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; human papillomavirus; long non-coding RNAs; microRNAs; non--coding RNAs.
Copyright © 2023 Guo, Yang, Li, Zhu, Chen, Pan, Long, Liu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of hub genes and potential therapeutic mechanisms related to HPV positive head and neck squamous carcinoma based on full transcriptomic detection and ceRNA network construction.Gene. 2024 Jun 5;910:148321. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148321. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Gene. 2024. PMID: 38428621
-
Role of non-coding RNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A narrative review.Oral Dis. 2018 Nov;24(8):1417-1427. doi: 10.1111/odi.12782. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Oral Dis. 2018. PMID: 28941018 Review.
-
EGFR-induced suppression of HPV E6/E7 is mediated by microRNA-9-5p silencing of BRD4 protein in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Nov 4;13(11):921. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05269-8. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36333293 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of human papillomavirus oncoproteins E6 and E7 inhibits invadopodia activity but promotes cell migration in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2018 Oct;1(3):e1125. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1125. Epub 2018 Jul 27. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2018. PMID: 32721084 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular mechanism of human papillomavirus-induced carcinogenesis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Clin Oncol. 2016 Oct;21(5):819-826. doi: 10.1007/s10147-016-1005-x. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Int J Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27339270 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Biomarkers in HPV-Positive Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Towards Precision Medicine.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jul 7;14(13):1448. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14131448. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging paradigms: unmasking the role of oxidative stress in HPV-induced carcinogenesis.Infect Agent Cancer. 2024 Jul 2;19(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s13027-024-00581-8. Infect Agent Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38956668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p63 orchestrates serine and one carbon metabolism enzymes expression in head and neck cancer.Biol Direct. 2023 Nov 9;18(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s13062-023-00426-1. Biol Direct. 2023. PMID: 37946250 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA EGOT Is the Marker of HPV Infection and a Prognostic Factor for HNSCC Patients.Biomedicines. 2025 Mar 26;13(4):798. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13040798. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40299341 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Transcript-Based Biomarkers Predicting Clinical Outcomes of HPV-Positive Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients.Cells. 2024 Jun 26;13(13):1107. doi: 10.3390/cells13131107. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38994960 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

