Opportunities and challenges of natural killer cell-derived extracellular vesicles
- PMID: 37064251
- PMCID: PMC10102538
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1122585
Opportunities and challenges of natural killer cell-derived extracellular vesicles
Abstract
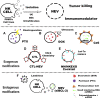
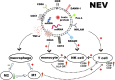
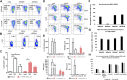
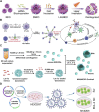
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are increasingly recognized as important intermediaries of intercellular communication. They have significant roles in many physiological and pathological processes and show great promise as novel biomarkers of disease, therapeutic agents, and drug delivery tools. Existing studies have shown that natural killer cell-derived EVs (NEVs) can directly kill tumor cells and participate in the crosstalk of immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. NEVs own identical cytotoxic proteins, cytotoxic receptors, and cytokines as NK cells, which is the biological basis for their application in antitumor therapy. The nanoscale size and natural targeting property of NEVs enable precisely killing tumor cells. Moreover, endowing NEVs with a variety of fascinating capabilities via common engineering strategies has become a crucial direction for future research. Thus, here we provide a brief overview of the characteristics and physiological functions of the various types of NEVs, focusing on their production, isolation, functional characterization, and engineering strategies for their promising application as a cell-free modality for tumor immunotherapy.
Keywords: cancer immunotherapy; engineering strategy; extracellular vesicles; natural killer cell; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2023 Qi, Zhao, Dong, Wang, Wang, Fan, Weng, Yu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Natural Killer Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Novel Players in Cancer Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2021 May 21;12:658698. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.658698. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34093547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles - New Strategies in Cancer Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 8;12:771551. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.771551. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34956197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil Extracellular Vesicles: A Delicate Balance between Pro-Inflammatory Responses and Anti-Inflammatory Therapies.Cells. 2022 Oct 21;11(20):3318. doi: 10.3390/cells11203318. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36291183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Professional killers: The role of extracellular vesicles in the reciprocal interactions between natural killer, CD8+ cytotoxic T-cells and tumour cells.J Extracell Vesicles. 2021 Apr;10(6):e12075. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12075. Epub 2021 Apr 1. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021. PMID: 33815694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Large-scale isolation and cytotoxicity of extracellular vesicles derived from activated human natural killer cells.J Extracell Vesicles. 2017 Feb 28;6(1):1294368. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2017.1294368. eCollection 2017. J Extracell Vesicles. 2017. PMID: 28326171 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Natural killer cell-derived exosomes for cancer immunotherapy: innovative therapeutics art.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Aug 5;23(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-02996-6. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37543612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetically engineered cell-derived nanovesicles for cancer immunotherapy.Nanoscale. 2024 May 2;16(17):8317-8334. doi: 10.1039/d3nr06565k. Nanoscale. 2024. PMID: 38592744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NK cells as powerful therapeutic tool in cancer immunotherapy.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024 Jun;47(3):733-757. doi: 10.1007/s13402-023-00909-3. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024. PMID: 38170381 Review.
-
Antitumor Immunity: Role of NK Cells and Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer Immunotherapy.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Dec 25;46(1):140-152. doi: 10.3390/cimb46010011. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 38248313 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aarsund M., Segers F. M., Wu Y., Inngjerdingen M. (2022). Comparison of characteristics and tumor targeting properties of extracellular vesicles derived from primary nk cells or nk-cell lines stimulated with il-15 or il-12/15/18. Cancer Immunology Immunotherapy.71 (9), 2227-2238. 10.1007/s00262-022-03161-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

