Does preoperative screening with computed tomography of the chest decrease risk of stroke in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting
- PMID: 37064355
- PMCID: PMC10102793
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-22-1047
Does preoperative screening with computed tomography of the chest decrease risk of stroke in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting
Abstract
Background: Stroke is one of the most feared complications post coronary artery bypass with aortic calcifications being the commonest source of embolic stroke. The aim of our study was to determine the clinical impact and usefulness of routine use of plain chest computerised tomography to screen for aortic calcification on incidence of postoperative stroke in coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) patients.
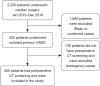
Methods: This is a retrospective case-control study that included four hundred and five patients who underwent primary isolated CABG and had preoperative plain chest computerised tomography as a screening for aortic calcification. Aortic calcification was classified according to the area involved (ascending, arch, arch vessels and descending aorta) and the pattern of calcification. Patients were divided into two groups according to the incidence of postoperative stroke and the aortic calcification distribution was compared between the two groups. Stroke predictors were studies using univariate and multivariate regression analysis.
Results: Fourteen patients (3.5%) developed postoperative stroke. There was no difference in preoperative and operative characteristics between patients who developed postoperative stroke and those who did not, except for the history of preoperative stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) that was higher in the group who developed postoperative stroke (50.00% vs. 6.19%, P<0.001). Patients who developed postoperative stroke had higher percentage of aortic root calcification (78.57% vs. 64.18%), ascending aortic calcification (28.57% vs. 19.07%) and descending aortic calcification (85.71% vs. 73.71%) but none of them reached statistical significance. History of preoperative stroke or TIA was the only significant predictor of postoperative stroke using both univariate and multivariate regression models.
Conclusions: Our study showed the importance of preoperative computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest as a screening tool as it detected a high prevalence of aortic calcification in our patients. However, its impact on prevention of postoperative stroke needs to be investigated further in future prospective studies.
Keywords: Chest computed tomography (chest CT); aortic calcification; coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG); stroke.
2023 Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://qims.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/qims-22-1047/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The relationship between aortic calcification on chest radiograph and neurocognitive impairment after coronary artery bypass grafting.Turk Gogus Kalp Damar Cerrahisi Derg. 2021 Apr 26;29(2):166-173. doi: 10.5606/tgkdc.dergisi.2021.21285. eCollection 2021 Apr. Turk Gogus Kalp Damar Cerrahisi Derg. 2021. PMID: 34104510 Free PMC article.
-
Who needs preoperative routine chest computed tomography for prevention of stroke in cardiac surgery?Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2010 Jul;11(1):30-3. doi: 10.1510/icvts.2009.231761. Epub 2010 Apr 1. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2010. PMID: 20360209
-
Impact of preoperative computed tomography scan on neurological outcomes in coronary artery bypass grafting patients: A propensity-score analysis.Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2024 Nov;32(8-9):443-450. doi: 10.1177/02184923241292098. Epub 2024 Oct 21. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2024. PMID: 39428858
-
Neurologic complications after off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting with and without aortic manipulation: meta-analysis of 11,398 cases from 8 studies.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011 Aug;142(2):e11-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2010.11.034. Epub 2011 Feb 1. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011. PMID: 21281950
-
Stroke and mortality rates after off-pump vs. pump-assisted/no-clamp coronary artery bypass grafting.J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2022 Dec;63(6):742-748. doi: 10.23736/S0021-9509.22.12337-2. Epub 2022 Sep 28. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2022. PMID: 36168952 Review.
References
-
- Goy JJ, Kaufmann U, Goy-Eggenberger D, et al. A prospective randomized trial comparing stenting to internal mammary artery grafting for proximal, isolated de novo left anterior coronary artery stenosis: the SIMA trial. Stenting vs Internal Mammary Artery. Mayo Clin Proc 2000;75:1116-23. 10.4065/75.11.1116 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources