Alterations in gut microbiota and urine metabolomics in infants with yin-deficiency constitution aged 0-2 years
- PMID: 37064462
- PMCID: PMC10102239
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14684
Alterations in gut microbiota and urine metabolomics in infants with yin-deficiency constitution aged 0-2 years
Abstract
Background: Based on the constitution theroy, infants are classified into balanced constitution (BC) and unbalanced constitution. Yin-deficiency constitution (YINDC) is a common type of unbalanced constitutions in Chinese infants. An infant's gut microbiota directly affects the child's health and has long-term effects on the maturation of the immune and endocrine systems throughout life. However, the gut microbiota of infants with YINDC remains unknown. Herein, we aimed to evaluate the intestinal flora profiles and urinary metabolites in infant with YINDC, find biomarkers to identify YINDC, and promote our understanding of infant constitution classification.
Methods: Constitutional Medicine Questionnaires were used to assess the infants' constitution types. 47 infants with 21 cases of YINDC and 26 cases of BC were included, and a cross-sectional sampling of stool and urine was conducted. Fecal microbiota was characterized using 16S rRNA sequencing, and urinary metabolomics was profiled using UPLC-Q-TOF/MS method. YINDC markers with high accuracy were identified using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis.
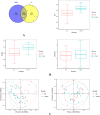
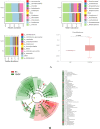
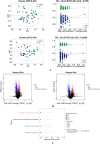
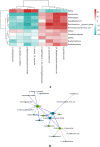
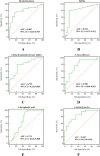
Results: The diversity and composition of intestinal flora and urinary metabolites differed significantly between the YINDC and BC groups. A total of 13 obviously different genera and 55 altered metabolites were identified. Stool microbiome shifts were associated with urine metabolite changes. A combined marker comprising two genera may have a high potential to identify YINDC with an AUC of 0.845.
Conclusions: Infants with YINDC had a unique gut microbiota and metabolomic profile resulting in a constitutional microclassification. The altered gut microbiome in YINDC may account for the higher risk of cardiovascular diseases. Metabolomic analysis of urine showed that metabolic pathways, including histidine metabolism, proximal tubule bicarbonate reclamation, arginine biosynthesis, and steroid hormone biosynthesis, were altered in infants with YINDC. Additionally, the combined bacterial biomarker had the ability to identify YINDC. Identifying YINDC in infancy and intervening at an early stage is crucial for preventing cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: Biomarker; Infant; Metabolomics; Microbiota; Traditional Chinese medicine; Yin deficiency constitution.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Damp-heat constitution influences gut microbiota and urine metabolism of Chinese infants.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 24;9(2):e12424. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12424. eCollection 2023 Feb. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36755610 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbial composition associated with risk of premature aging in women with Yin-deficiency constitution.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jan 3;14:1500959. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1500959. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39831109 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship of CCL4, BCL2A1, and NFKBIA genes with premature aging in women of Yin deficiency constitution.Exp Gerontol. 2021 Jul 1;149:111316. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2021.111316. Epub 2021 Mar 23. Exp Gerontol. 2021. PMID: 33766622
-
Integrative analysis of microbiota and metabolomics in individuals exhibiting different TCM constitutions utilizing 16S rDNA sequencing and LC/MS metabolomics.Microb Pathog. 2025 Aug;205:107621. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2025.107621. Epub 2025 Apr 19. Microb Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40258500
-
The Metagenomic and Metabolomic Profile of the Infantile Gut: Can They Be "Predicted" by the Feed Type?Children (Basel). 2022 Jan 25;9(2):154. doi: 10.3390/children9020154. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204875 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Different Traditional Chinese Medicine Constitutions on the Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant: A Retrospective Observational Study.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Sep 25;16:6333-6344. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S424176. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37780533 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine constitution and sarcopenia: a cross-sectional study.Front Public Health. 2024 Jul 24;12:1368933. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1368933. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39114511 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang Q. People's Health Publishing House; Beijing: 2009. Constitution of Chinese Medicine (2008) pp. 159–175.
-
- Li Z. Beijing University of Chinese Medicine; Beijing: 2021. Compilation and Evaluation of Wang Qi's Nine Body Types in Constitutional Medicine Questionnaire (0-3 Years Version)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

