Effects of lncRNA HOXA11-AS on Sevoflurane-Induced Neuronal Apoptosis and Inflammatory Responses by Regulating miR-98-5p/EphA4
- PMID: 37064501
- PMCID: PMC10098412
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/7750134
Effects of lncRNA HOXA11-AS on Sevoflurane-Induced Neuronal Apoptosis and Inflammatory Responses by Regulating miR-98-5p/EphA4
Abstract
Objective: To explore the molecular mechanism of sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity and to determine whether lncRNA HOXA11-AS affects sevoflurane-induced neuronal apoptosis and inflammation by regulating miR-98-5p/EphA4.
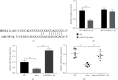
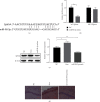
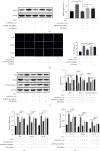
Methods: Morris water maze (MWM) test was used to detect the learning and memory ability of rats, HE staining was used to observe hippocampal pathology, TUNEL staining was used to detect the level of neuronal apoptosis, and RT-qPCR was used to detect the expression of HOXA11-AS, miR-98-5p, IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α. At the same time, the contents of IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α in serum were detected by ELISA. The expressions of apoptosis-related proteins EphA4, Bax, Cleaved caspase 3, and Bcl-2 were detected by Western blot. The dual-luciferase gene reporter verified the targeting relationship between HOXA11-AS and miR-98-5p and the targeting relationship between miR-98-5p and EphA4.
Results: The expression of HOXA11-AS was observed in sevoflurane-treated rats or cells and promoted neuronal apoptosis and inflammation. HOXA11-AS was knocked out alone, or miR-98-5p was overexpressed which attenuates neuronal apoptosis and inflammatory inflammation after sevoflurane treatment. Furthermore, knockdown of HOXA11-AS alone was partially restored by knockdown of miR-98-5p or overexpression of EphA4.
Conclusion: Inhibition of lncRNA HOXA11-AS attenuates sevoflurane-induced neuronal apoptosis and inflammatory responses via miR-98-5p/EphA4.
Copyright © 2023 Li Zhao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Knockdown of lncRNA NKILA suppresses sevoflurane-induced neuronal cell injury partially by targeting miR-205-5p/ELAVL1 axis.Gen Physiol Biophys. 2023 May;42(3):285-295. doi: 10.4149/gpb_2023007. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2023. PMID: 37098737
-
miR-182-5p Delivered by Plasma Exosomes Promotes Sevoflurane-Induced Neuroinflammation and Cognitive Dysfunction in Aged Rats with Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction by Targeting Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Activating NF-κB Pathway.Neurotox Res. 2022 Dec;40(6):1902-1912. doi: 10.1007/s12640-022-00597-1. Epub 2022 Oct 29. Neurotox Res. 2022. PMID: 36308704
-
LncRNA NEAT1 affects inflammatory response by targeting miR-129-5p and regulating Notch signaling pathway in epilepsy.Cell Cycle. 2020 Feb;19(4):419-431. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1711578. Epub 2020 Jan 17. Cell Cycle. 2020. PMID: 31948324 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA DLGAP4 alleviates sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity by regulating miR-9-5p/Sirt1/BDNF pathway.Exp Cell Res. 2023 Dec 15;433(2):113861. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2023.113861. Epub 2023 Nov 23. Exp Cell Res. 2023. PMID: 38000773
-
MicroRNA-204-5p mediates sevoflurane-induced cytotoxicity in HT22 cells by targeting brain-derived neurotrophic factor.Histol Histopathol. 2020 Nov;35(11):1353-1361. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-266. Epub 2020 Oct 2. Histol Histopathol. 2020. PMID: 33006132
Cited by
-
The SAP130/Mincle axis was involved in sevoflurane-induced neuronal death and microglial activation in juvenile mice.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 28;16:1647329. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1647329. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40792209 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA PART1 improves sevoflurane-induced impairments in learning and cognitive function by regulating miR-16-5p expression and reducing neuroinflammation.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2025 Jan 26;14(1):tfaf009. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfaf009. eCollection 2025 Feb. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2025. PMID: 39872305
-
Silencing CircHIPK3 improves sevoflurane-explore learning and memory dysfunction and nerve damage via enhancing miR-338-3p.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024 Aug 19;13(4):tfae132. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfae132. eCollection 2024 Aug. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024. PMID: 39165832 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the hidden dangers: a review of non-apoptotic programmed cell death in anesthetic-induced developmental neurotoxicity.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Aug 2;40(1):63. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09895-0. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39093513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Schwann Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Isolation, Bioactivity Assessment, and Omics Characterization.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Apr 4;20:4123-4144. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S500159. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40201152 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

