Epidemiological characteristics of overseas imported COVID-19 cases into China: A scoping literature review
- PMID: 37064698
- PMCID: PMC10090422
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1143468
Epidemiological characteristics of overseas imported COVID-19 cases into China: A scoping literature review
Abstract
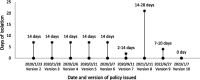
Previous studies investigating the characteristics of imported cases were mostly limited to a certain province/city or a specific sub-group during a certain period with a small sample size, which may not provide an overall picture of the characteristics of imported cases. In this scoping literature review, we comprehensively synthesized the epidemiological characteristics of overseas imported COVID-19 cases into China by retrieving six literature databases, with aims to provide implications for more targeted control, prevention, and medical treatment of this disease. After dropping duplicates and reviewing titles, abstracts, and full-texts, 50 articles were included in the review finally, including 26 (52%) articles in English and 24 (48%) articles in Chinese. According to the type of data sources, the 50 studies were divided into three categories: 13 (26%) articles using data sourced from the Chinese Infectious Diseases Online Reporting System, 15 (30%) articles using data from the websites of national/local health departments, and 22 (44%) articles using hospital admission data. Most of the overseas imported COVID-19 cases were young and middle-aged Chinese students and businessmen returning from the United States, Europe, and some neighboring countries. Airport routine health screening measures could not identify COVID-cases effectively, although scheduled multiple nucleic acid tests were required before boarding. Almost all imported cases were identified during the hotel quarantine period. Although a large proportion of imported cases were asymptomatic or with mild symptoms in the published literature, they may be due to participant selection bias. The exact proportion of asymptomatic cases may need to be further investigated especially through population-based large-scale studies.
Keywords: COVID-19; China; epidemiological characteristics; imported; review.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Chen, Li, Yang, Chen, Lin, Xiao, Ma, Wu, Liu, Xu and Xiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) . WHO director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19. (2020) Available at: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-genera... (Accessed January 10, 2023).
-
- Central People's Government of the People's Republic of China (2020). Notice on further reduction of international flights to China during the period of COVID-19 pandemic. Available at: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-03/27/content_5496232.htm (Accessed January 10, 2023).
-
- National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China (2023). Notice on further optimizing and implementing the prevention and control measures of COVID-19 epidemic. Available at: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/zhengcwj/202212/8278e7a7aee34e5bb378f0e0fc94e0... (Accessed January 10, 2023).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical