Surface charge adaptive nitric oxide nanogenerator for enhanced photothermal eradication of drug-resistant biofilm infections
- PMID: 37064802
- PMCID: PMC10091033
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.03.022
Surface charge adaptive nitric oxide nanogenerator for enhanced photothermal eradication of drug-resistant biofilm infections
Abstract
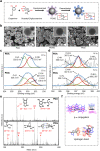
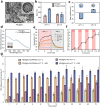
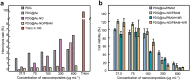
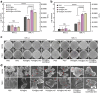
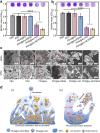
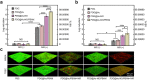
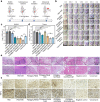
Due to protection of extracellular polymeric substances, the therapeutic efficiency of conventional antimicrobial agents is often impeded by their poor infiltration and accumulation in biofilm. Herein, one type of surface charge adaptable nitric oxide (NO) nanogenerator was developed for biofilm permeation, retention and eradication. This nanogenerator (PDG@Au-NO/PBAM) is composed of a core-shell structure: thermo-sensitive NO donor conjugated AuNPs on cationic poly(dopamine-co-glucosamine) nanoparticle (PDG@Au-NO) served as core, and anionic phenylboronic acid-acryloylmorpholine (PBAM) copolymer was employed as a shell. The NO nanogenerator featured long circulation and good biocompatibility. Once the nanogenerator reached acidic biofilm, its surface charge would be switched to positive after shell dissociation and cationic core exposure, which was conducive for the nanogenerator to infiltrate and accumulate in the depth of biofilm. In addition, the nanogenerator could sustainably generate NO to disturb the integrity of biofilm at physiological temperature, then generate hyperthermia and explosive NO release upon NIR irradiation to efficiently eradicate drug-resistant bacteria biofilm. Such rational design offers a promising approach for developing nanosystems against biofilm-associated infections.
Keywords: Antibacterial; Biofilm microenvironment; Charge reversal; Gasotransmitter; Photothermal therapy.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Surface Charge Switchable Supramolecular Nanocarriers for Nitric Oxide Synergistic Photodynamic Eradication of Biofilms.ACS Nano. 2020 Jan 28;14(1):347-359. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b05493. Epub 2020 Jan 6. ACS Nano. 2020. PMID: 31887012
-
Photoactivatable Nitric Oxide-Releasing Gold Nanocages for Enhanced Hyperthermia Treatment of Biofilm-Associated Infections.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021 Nov 3;13(43):50668-50681. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c12483. Epub 2021 Oct 20. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021. PMID: 34669372
-
Surface-Adaptive Gold Nanoparticles with Effective Adherence and Enhanced Photothermal Ablation of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm.ACS Nano. 2017 Sep 26;11(9):9330-9339. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b04731. Epub 2017 Aug 17. ACS Nano. 2017. PMID: 28806528
-
Nanotechnology as a therapeutic tool to combat microbial resistance.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013 Nov;65(13-14):1803-15. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2013.07.011. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013. PMID: 23892192 Review.
-
Recent Developments in Nitric Oxide Donors and Delivery for Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Applications.Molecules. 2022 Jan 20;27(3):674. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030674. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35163933 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Photothermal/Photoacoustic Therapy Combined with Metal-Based Nanomaterials for the Treatment of Microbial Infections.Microorganisms. 2023 Aug 14;11(8):2084. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11082084. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37630644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy inhibition mediated via an injectable and NO-releasing hydrogel for amplifying the antitumor efficacy of mild magnetic hyperthermia.Bioact Mater. 2024 May 25;39:336-353. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.05.032. eCollection 2024 Sep. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 38827171 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced biomaterials for targeting mature biofilms in periodontitis therapy.Bioact Mater. 2025 Feb 27;48:474-492. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.02.026. eCollection 2025 Jun. Bioact Mater. 2025. PMID: 40093304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D-printed advanced scaffold armed with exosomes derived from human skeletal stem cell identified by single-cell RNA sequencing enhances osteochondral regeneration.Bioact Mater. 2025 May 14;51:231-256. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.04.028. eCollection 2025 Sep. Bioact Mater. 2025. PMID: 40487240 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in nanomaterials and their mechanisms for infected wounds management.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Feb 4;31:101553. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101553. eCollection 2025 Apr. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40182659 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Willyard C. The drug-resistant bacteria that pose the greatest health threats. Nature. 2017;543 15-15. - PubMed
-
- Flemming H.-C., Wingender J., Szewzyk U., Steinberg P., Rice S., Kjelleberg S. Biofilms: an emergent form of bacterial life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016;14:563–575. - PubMed
-
- Flemming H.-C., Wingender J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010;8:623–633. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

