Cirrhosis-induced oxidative stress in erythrocytes: The therapeutic potential of taurine
- PMID: 37064835
- PMCID: PMC10090995
- DOI: 10.5114/ceh.2023.126028
Cirrhosis-induced oxidative stress in erythrocytes: The therapeutic potential of taurine
Abstract
Aim of the study: Cholestasis/cirrhosis could induce erythrocyte lysis. The incidence of various types of anemia in cirrhosis is approx. 75%. Several studies have mentioned the pivotal role of oxidative stress in this complication. Taurine (TAU) is the human body's most abundant free amino acid. TAU is known as a robust cell membrane stabilizer. Many studies have mentioned that TAU could counteract oxidative stress in various experimental models. The current study was intended to evaluate the effect of TAU on erythrocytes in cirrhotic rats.
Material and methods: Bile duct ligation (BDL) surgery was carried out on rats. Then, complete blood count (CBC), hemoglobin (Hgb), hematocrit (HTC), and erythrocytes' G6PD, catalase (CAT), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity were measured. Moreover, biomarkers of oxidative stress were assessed, and the erythrocytes' morphological changes were monitored in the cirrhotic mice exposed to TAU (0.25%, 0.5%, and 1% w : v in drinking water).
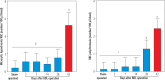
Results: Significant changes in the assessed erythrocyte parameters (G6PD activity, Hgb, HTC, and erythrocyte count) and red blood cells (RBC) morphological alterations were detected on day 42 after BDL surgery. Biomarkers of oxidative stress also did not change at the time points, except on post-BDL days 28 and 42. A significant decrease in blood parameters was evident at post-BDL day 42. All doses of TAU (0.25%, 0.5%, and 1% w : v in drinking water) significantly improved erythrocyte parameters and encountered oxidative stress in the erythrocytes of cirrhotic animals.
Conclusions: These data indicate that TAU could be a safe agent to mitigate cirrhosis-induced erythrocyte damage and anemia. Further investigations are necessary to prove this in clinical settings.
Keywords: anemia; bile acids; cholestasis; cirrhosis; oxidative stress; red blood cells.
Copyright © 2023 Clinical and Experimental Hepatology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Taurine mitigates the development of pulmonary inflammation, oxidative stress, and histopathological alterations in a rat model of bile duct ligation.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022 Dec;395(12):1557-1572. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02291-7. Epub 2022 Sep 13. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36097067
-
Cellular and mitochondrial taurine depletion in bile duct ligated rats: a justification for taurine supplementation in cholestasis/cirrhosis.Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022 Sep;8(3):195-210. doi: 10.5114/ceh.2022.119216. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 36685263 Free PMC article.
-
Taurine mitigates bile duct obstruction-associated cholemic nephropathy: effect on oxidative stress and mitochondrial parameters.Clin Exp Hepatol. 2021 Mar;7(1):30-40. doi: 10.5114/ceh.2021.104675. Epub 2021 Mar 25. Clin Exp Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34027113 Free PMC article.
-
Taurine supplementation abates cirrhosis-associated locomotor dysfunction.Clin Exp Hepatol. 2018 Jun;4(2):72-82. doi: 10.5114/ceh.2018.75956. Epub 2018 May 25. Clin Exp Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29904723 Free PMC article.
-
Taurine mitigates cirrhosis-associated heart injury through mitochondrial-dependent and antioxidative mechanisms.Clin Exp Hepatol. 2020 Sep;6(3):207-219. doi: 10.5114/ceh.2020.99513. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Clin Exp Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 33145427 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Adverse hematological profiles associated with chlorpromazine antipsychotic treatment in male rats: Preventive and reversal mechanisms of taurine and coenzyme-Q10.Toxicol Rep. 2024 Apr 20;12:448-462. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.04.004. eCollection 2024 Jun. Toxicol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38693965 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Role of Taurine in Aging and Cardiovascular Health: An Updated Overview.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 30;15(19):4236. doi: 10.3390/nu15194236. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37836520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Protective Effects of Taurine, a Non-essential Amino Acid, Against Metals Toxicities: A Review Article.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Feb;203(2):872-890. doi: 10.1007/s12011-024-04191-8. Epub 2024 May 13. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 38735894 Review.
References
-
- Heidari R, Moezi L, Asadi B, et al. . Hepatoprotective effect of boldine in a bile duct ligated rat model of cholestasis/cirrhosis. Pharma Nutrition 2017; 5: 109-117.
-
- Ommati MM, Farshad O, Niknahad H, et al. . Cholestasis-associated reproductive toxicity in male and female rats: The fundamental role of mitochondrial impairment and oxidative stress. Toxicol Lett 2019; 316: 60-72. - PubMed
-
- Ommati MM, Mohammadi H, Mousavi K, et al. . Metformin alleviates cholestasis-associated nephropathy through regulating oxidative stress and mitochondrial function. Liver Res 2021; 5: 171-180.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
