Distinct microRNA and protein profiles of extracellular vesicles secreted from myotubes from morbidly obese donors with type 2 diabetes in response to electrical pulse stimulation
- PMID: 37064893
- PMCID: PMC10098097
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1143966
Distinct microRNA and protein profiles of extracellular vesicles secreted from myotubes from morbidly obese donors with type 2 diabetes in response to electrical pulse stimulation
Abstract
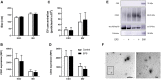
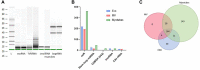
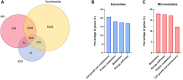
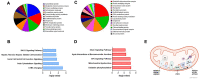
Lifestyle disorders like obesity, type 2 diabetes (T2D), and cardiovascular diseases can be prevented and treated by regular physical activity. During exercise, skeletal muscles release signaling factors that communicate with other organs and mediate beneficial effects of exercise. These factors include myokines, metabolites, and extracellular vesicles (EVs). In the present study, we have examined how electrical pulse stimulation (EPS) of myotubes, a model of exercise, affects the cargo of released EVs. Chronic low frequency EPS was applied for 24 h to human myotubes isolated and differentiated from biopsy samples from six morbidly obese females with T2D, and EVs, both exosomes and microvesicles (MV), were isolated from cell media 24 h thereafter. Size and concentration of EV subtypes were characterized by nanoparticle tracking analysis, surface markers were examined by flow cytometry and Western blotting, and morphology was confirmed by transmission electron microscopy. Protein content was assessed by high-resolution proteomic analysis (LC-MS/MS), non-coding RNA was quantified by Affymetrix microarray, and selected microRNAs (miRs) validated by real time RT-qPCR. The size and concentration of exosomes and MV were unaffected by EPS. Of the 400 miRs identified in the EVs, EPS significantly changed the level of 15 exosome miRs, of which miR-1233-5p showed the highest fold change. The miR pattern of MV was unaffected by EPS. Totally, about 1000 proteins were identified in exosomes and 2000 in MV. EPS changed the content of 73 proteins in exosomes, 97 in MVs, and of these four were changed in both exosomes and MV (GANAB, HSPA9, CNDP2, and ATP5B). By matching the EPS-changed miRs and proteins in exosomes, 31 targets were identified, and among these several promising signaling factors. Of particular interest were CNDP2, an enzyme that generates the appetite regulatory metabolite Lac-Phe, and miR-4433b-3p, which targets CNDP2. Several of the regulated miRs, such as miR-92b-5p, miR-320b, and miR-1233-5p might also mediate interesting signaling functions. In conclusion, we have used a combined transcriptome-proteome approach to describe how EPS affected the cargo of EVs derived from myotubes from morbidly obese patients with T2D, and revealed several new factors, both miRs and proteins, that might act as exercise factors.
Keywords: electrical pulse stimulation (EPS); extracellular vescicles; human myotubes; microRNA; morbid obesity; proteomic; transcriptomic; type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Copyright © 2023 Aas, Øvstebø, Brusletto, Aspelin, Trøseid, Qureshi, Eid, Olstad, Nyman and Haug.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterizing Extracellular Vesicles and Particles Derived from Skeletal Muscle Myoblasts and Myotubes and the Effect of Acute Contractile Activity.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Apr 26;12(5):464. doi: 10.3390/membranes12050464. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35629791 Free PMC article.
-
Electrical pulse stimulation-induced tetanic exercise simulation increases the secretion of extracellular vesicles from C2C12 myotubes.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023 Sep 10;672:177-184. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.06.054. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023. PMID: 37354611
-
The RNA-binding protein hnRNPU regulates the sorting of microRNA-30c-5p into large extracellular vesicles.J Extracell Vesicles. 2020 Jul 2;9(1):1786967. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2020.1786967. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020. PMID: 32944175 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating exosomal microRNAs as emerging non-invasive clinical biomarkers in heart failure: Mega bio-roles of a nano bio-particle.IUBMB Life. 2020 Dec;72(12):2546-2562. doi: 10.1002/iub.2396. Epub 2020 Oct 14. IUBMB Life. 2020. PMID: 33053610 Review.
-
Exosomes as Mediators of the Systemic Adaptations to Endurance Exercise.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018 Mar 1;8(3):a029827. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a029827. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018. PMID: 28490541 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic effects of platelet-derived extracellular vesicles on viral myocarditis correlate with biomolecular content.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 6;15:1468969. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1468969. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39835120 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of MicroRNAs and Exosomal MicroRNAs after Dietary Interventions for Obesity and Insulin Resistance: A Narrative Review.Metabolites. 2023 Dec 7;13(12):1190. doi: 10.3390/metabo13121190. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 38132872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood biomarker fingerprints in a cohort of patients with CHRNE-related congenital myasthenic syndrome.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025 Feb 13;13(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s40478-025-01946-9. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025. PMID: 39948634 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modifications in obesity-associated diseases.MedComm (2020). 2024 Feb 24;5(2):e496. doi: 10.1002/mco2.496. eCollection 2024 Feb. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 38405061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CNDP2: An Enzyme Linking Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases?J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2025 Feb;18(1):48-57. doi: 10.1007/s12265-024-10560-4. Epub 2024 Sep 30. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 39349903 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

