Effects of supplemental fulvic acid on survival, growth performance, digestive ability and immunity of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae
- PMID: 37064905
- PMCID: PMC10102811
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1159320
Effects of supplemental fulvic acid on survival, growth performance, digestive ability and immunity of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae
Abstract
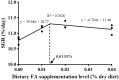
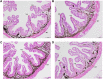
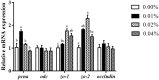
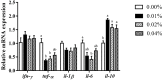
A 30-day feeding trial was designed to evaluate the effect of supplemental fulvic acid (FA) on survival, growth performance, digestive ability and immunity of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae (initial body weight 11.33 ± 0.57 mg). Four isonitrogenous and isolipids diets containing 0.00%, 0.01%, 0.02% and 0.04% FA were formulated, respectively. Results showed that the supplementation of 0.04% FA significantly improved survival rate of large yellow croaker larvae. Meanwhile, supplemental FA significantly increased final body weight and specific growth rate. Based on the specific growth rate, the optimal supplementation was 0.0135% FA. Larvae fed the diet with 0.01% FA had significantly higher villus height than the control. The supplementation of 0.01%-0.02% FA significantly increased the muscular thickness of intestine. Moreover, supplementation of FA significantly increased mRNA expression of intestinal epithelial proliferation and barrier genes (pcna, zo-1 and zo-2). Diets supplemented with 0.02%-0.04% FA significantly increased the activity of trypsin in the intestinal segment, while 0.01%-0.02% FA significantly increased the activity of trypsin in the pancreatic segment. Compared with the control, supplementation of FA remarkably increased activities of alkaline phosphatase and leucine aminopeptidase in the brush border membrane of intestine. Larvae fed the diet with 0.01% FA significantly increased activities of lysozyme and total nitric oxide synthase. Furthermore, the supplementation of 0.01% to 0.02% FA significantly decreased the mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (tnf-α and il-6). Concurrently, supplemental FA significantly increased anti-inflammatory cytokine (il-10) mRNA expression level. In conclusion, this study indicated that the supplementation of FA could improve the survival rate and growth performance of larvae by promoting intestinal development, digestive enzymes activities and innate immunity.
Keywords: fulvic acid; immune response; intestinal morphology; large yellow croaker; larval nutrition.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Liu, Yao, Zhang, Wang, Liu, Hong, Mai and Ai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
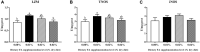
Similar articles
-
Effects of supplemental ferulic acid (FA) on survival, growth performance, digestive enzyme activities, antioxidant capacity and lipid metabolism of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae.Fish Physiol Biochem. 2022 Dec;48(6):1635-1648. doi: 10.1007/s10695-022-01120-1. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2022. PMID: 36178594
-
Effects of dietary succinic acid supplementation on growth performance, digestive ability, intestinal development and immunity of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024 Dec;155:109972. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109972. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39423905
-
Effects of Chitosan-Coated Microdiet on Dietary Physical Properties, Growth Performance, Digestive Enzyme Activities, Antioxidant Capacity, and Inflammation Response of Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Larvae.Aquac Nutr. 2022 Sep 5;2022:4355182. doi: 10.1155/2022/4355182. eCollection 2022. Aquac Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36860430 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Allicin Improved the Survival and Growth of Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Larvae via Promoting Intestinal Development, Alleviating Inflammation and Enhancing Appetite.Front Physiol. 2020 Oct 9;11:587674. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.587674. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33162901 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dietary eucommia ulmoides leaf extract on growth performance, expression of feeding-related genes, activities of digestive enzymes, antioxidant capacity, immunity and cytokines expression of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae.Br J Nutr. 2022 Nov 14;128(9):1711-1719. doi: 10.1017/S0007114521004621. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Br J Nutr. 2022. PMID: 34789344
References
-
- Ai Q., Zhao J., Mai K., Xu W., Tan B., Ma H., et al. (2008). Optimal dietary lipid level for large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) larvae. Aquac. Nutr. 14, 515–522. 10.1111/j.1365-2095.2007.00557.x - DOI
-
- Bai H., Chang Q., Shi B., Shan A. (2013). Effects of fulvic acid on growth performance and meat quality in growing-finishing pigs. Livest. Sci. 158, 118–123. 10.1016/j.livsci.2013.10.013 - DOI
-
- Cahu C. L., Infante J. L. Z. (1994). Early weaning of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larvae with a compound diet: Effect on digestive enzymes. Cony. Eiochent. Plty. 109, 213–222. 10.1016/0300-9629(94)90123-6 - DOI
-
- Cai Z., Xie F. J., Mai K., Ai Q. (2017). Molecular cloning and genetic ontogeny of some key lipolytic enzymes in large yellow croaker larvae (Larimichthys crocea R.). Aquac. Res. 48, 1183–1193. 10.1111/are.12960 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

