Improving the genetic system for Halorubrum lacusprofundi to allow in-frame deletions
- PMID: 37065119
- PMCID: PMC10102395
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1095621
Improving the genetic system for Halorubrum lacusprofundi to allow in-frame deletions
Abstract
Halorubrum lacusprofundi is a cold-adapted halophilic archaeon isolated from Deep Lake, Antarctica. Hrr. lacusprofundi is commonly used to study adaptation to cold environments and thereby a potential source for biotechnological products. Additionally, in contrast to other haloarchaeal model organisms, Hrr. lacusprofundi is also susceptible to a range of different viruses and virus-like elements, making it a great model to study virus-host interactions in a cold-adapted organism. A genetic system has previously been reported for Hrr. lacusprofundi; however, it does not allow in-frame deletions and multiple gene knockouts. Here, we report the successful generation of uracil auxotrophic (pyrE2) mutants of two strains of Hrr. lacusprofundi. Subsequently, we attempted to generate knockout mutants using the auxotrophic marker for selection. However, surprisingly, only the combination of the auxotrophic marker and antibiotic selection allowed the timely and clean in-frame deletion of a target gene. Finally, we show that vectors established for the model organism Haloferax volcanii are deployable for genetic manipulation of Hrr. lacusprofundi, allowing the use of the portfolio of genetic tools available for H. volcanii in Hrr. lacusprofundi.
Keywords: Halorubrum lacusprofundi; archaea; auxotrophic mutant; cold adaptation; genetic system; haloarchaea.
Copyright © 2023 Gebhard, Duggin and Erdmann.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
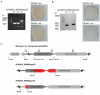


References
-
- Alarcón-Schumacher T., Naor A., Gophna U., Erdmann S. (2022). Isolation of a virus causing a chronic infection in the archaeal model organism Haloferax volcanii reveals antiviral activities of a provirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 119:e2205037119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2205037119, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

