Intra-osseous plasma rich in growth factors enhances cartilage and subchondral bone regeneration in rabbits with acute full thickness chondral defects: Histological assessment
- PMID: 37065219
- PMCID: PMC10095833
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1131666
Intra-osseous plasma rich in growth factors enhances cartilage and subchondral bone regeneration in rabbits with acute full thickness chondral defects: Histological assessment
Abstract
Background: Intra-articular (IA) combined with intra-osseous (IO) infiltration of plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF) have been proposed as an alternative approach to treat patients with severe osteoarthritis (OA) and subchondral bone damage. The aim of the study is to evaluate the efficacy of IO injections of PRGF to treat acute full depth chondral lesion in a rabbit model by using two histological validated scales (OARSI and ICRS II).
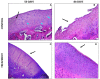
Methodology: A total of 40 rabbits were included in the study. A full depth chondral defect was created in the medial femoral condyle and then animals were divided into 2 groups depending on the IO treatment injected on surgery day: control group (IA injection of PRGF and IO injection of saline) and treatment group (IA combined with IO injection of PRGF). Animals were euthanized 56 and 84 days after surgery and the condyles were processed for posterior histological evaluation.
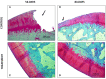
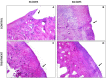
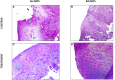
Results: Better scores were obtained in treatment group in both scoring systems at 56- and 84-days follow-up than in control group. Additionally, longer-term histological benefits have been obtained in the treatment group.
Conclusions: The results suggests that IO infiltration of PRGF enhances cartilage and subchondral bone healing more than the IA-only PRGF infiltration and provides longer-lasting beneficial effects.
Keywords: articular cartilage; bioregenerative therapies; chondral defect; growth factors; histology; osteoarthritis; platelet rich plasma.
Copyright © 2023 Torres-Torrillas, Damia, Romero, Pelaez, Miguel-Pastor, Chicharro, Carrillo, Rubio and Sopena.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Treating Full Depth Cartilage Defects with Intraosseous Infiltration of Plasma Rich in Growth Factors: An Experimental Study in Rabbits.Cartilage. 2021 Dec;13(2_suppl):766S-773S. doi: 10.1177/19476035211057246. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Cartilage. 2021. PMID: 34861782 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-osseous infiltration of adipose mesenchymal stromal cells and plasma rich in growth factors to treat acute full depth cartilage defects in a rabbit model: Serum osteoarthritis biomarkers and macroscopical assessment.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Dec 20;9:1057079. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1057079. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36605767 Free PMC article.
-
The Combined Intraosseous Administration of Orthobiologics Outperformed Isolated Intra-articular Injections in Alleviating Pain and Cartilage Degeneration in a Rat Model of MIA-Induced Knee Osteoarthritis.Am J Sports Med. 2024 Jan;52(1):140-154. doi: 10.1177/03635465231212668. Am J Sports Med. 2024. PMID: 38164685
-
Single intra-articular injection with or without intra-osseous injections of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of osteoarthritis knee: A single-blind, randomized clinical trial.Injury. 2022 Mar;53(3):1247-1253. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2022.01.012. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Injury. 2022. PMID: 35033356 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of clinical outcome, cartilage turnover, and inflammatory activity following either intra-articular or a combination of intra-articular with intra-osseous platelet-rich plasma injections in osteoarthritis knee: A randomized, clinical trial.Injury. 2023 Feb;54(2):728-737. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2022.11.036. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Injury. 2023. PMID: 36414504 Clinical Trial.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

