As without, so within: how the brain's temporo-spatial alignment to the environment shapes consciousness
- PMID: 37065263
- PMCID: PMC10102730
- DOI: 10.1098/rsfs.2022.0076
As without, so within: how the brain's temporo-spatial alignment to the environment shapes consciousness
Abstract
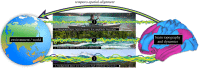
Consciousness is constituted by a structure that includes contents as foreground and the environment as background. This structural relation between the experiential foreground and background presupposes a relationship between the brain and the environment, often neglected in theories of consciousness. The temporo-spatial theory of consciousness addresses the brain-environment relation by a concept labelled 'temporo-spatial alignment'. Briefly, temporo-spatial alignment refers to the brain's neuronal activity's interaction with and adaption to interoceptive bodily and exteroceptive environmental stimuli, including their symmetry as key for consciousness. Combining theory and empirical data, this article attempts to demonstrate the yet unclear neuro-phenomenal mechanisms of temporo-spatial alignment. First, we suggest three neuronal layers of the brain's temporo-spatial alignment to the environment. These neuronal layers span across a continuum from longer to shorter timescales. (i) The background layer comprises longer and more powerful timescales mediating topographic-dynamic similarities between different subjects' brains. (ii) The intermediate layer includes a mixture of medium-scaled timescales allowing for stochastic matching between environmental inputs and neuronal activity through the brain's intrinsic neuronal timescales and temporal receptive windows. (iii) The foreground layer comprises shorter and less powerful timescales for neuronal entrainment of stimuli temporal onset through neuronal phase shifting and resetting. Second, we elaborate on how the three neuronal layers of temporo-spatial alignment correspond to their respective phenomenal layers of consciousness. (i) The inter-subjectively shared contextual background of consciousness. (ii) An intermediate layer that mediates the relationship between different contents of consciousness. (iii) A foreground layer that includes specific fast-changing contents of consciousness. Overall, temporo-spatial alignment may provide a mechanism whose different neuronal layers modulate corresponding phenomenal layers of consciousness. Temporo-spatial alignment can provide a bridging principle for linking physical-energetic (free energy), dynamic (symmetry), neuronal (three layers of distinct time-space scales) and phenomenal (form featured by background-intermediate-foreground) mechanisms of consciousness.
Keywords: consciousness; spatio-temporal neuroscience; temporo-spatial dynamics.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
From Shorter to Longer Timescales: Converging Integrated Information Theory (IIT) with the Temporo-Spatial Theory of Consciousness (TTC).Entropy (Basel). 2022 Feb 13;24(2):270. doi: 10.3390/e24020270. Entropy (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205564 Free PMC article.
-
Temporo-spatial Theory of Consciousness (TTC) - Bridging the gap of neuronal activity and phenomenal states.Behav Brain Res. 2022 Apr 29;424:113788. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2022.113788. Epub 2022 Feb 8. Behav Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 35149122 Review.
-
How do the brain's time and space mediate consciousness and its different dimensions? Temporo-spatial theory of consciousness (TTC).Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2017 Sep;80:630-645. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.07.013. Epub 2017 Jul 28. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2017. PMID: 28760626 Review.
-
Is temporo-spatial dynamics the "common currency" of brain and mind? In Quest of "Spatiotemporal Neuroscience".Phys Life Rev. 2020 Jul;33:34-54. doi: 10.1016/j.plrev.2019.05.002. Epub 2019 May 23. Phys Life Rev. 2020. PMID: 31221604 Review.
-
Scale-free dynamics in the core-periphery topography and task alignment decline from conscious to unconscious states.Commun Biol. 2023 May 9;6(1):499. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-04879-y. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37161021 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
From the brain's encoding of input dynamics to its behavior: neural dynamics shape bias in decision making.Commun Biol. 2024 Nov 19;7(1):1538. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07235-w. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39562707 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic mechanisms that couple the brain and breathing to the external environment.Commun Biol. 2024 Aug 3;7(1):938. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06642-3. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39097670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The hidden structure of consciousness.Front Psychol. 2024 Apr 8;15:1344033. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1344033. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38650907 Free PMC article.
-
Approaching the nature of consciousness through a phenomenal analysis of early vision. What is the explanandum?Front Psychol. 2024 Mar 18;15:1329259. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1329259. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38562232 Free PMC article.
-
Task difficulty modulates the effect of mind wandering on phase dynamics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jun 3;122(22):e2416387122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2416387122. Epub 2025 May 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40445764 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Northoff G. 2013. Unlocking the brain, vol. 1: coding. New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

