Narrowing the therapeutic window?-A case-control study on the influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on the primary UICC stage of NSCLC
- PMID: 37065553
- PMCID: PMC10089851
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-22-1091
Narrowing the therapeutic window?-A case-control study on the influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on the primary UICC stage of NSCLC
Abstract
Background: General clinical perception suggests a decline in the diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. Early diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is crucial in therapeutic regimes as early stages are potentially curable by operation alone or with combined therapy. Pandemic-triggered overload of the healthcare system may have prolonged the diagnosis of NSCLC, possibly leading to higher tumor stages at first diagnosis. This study aims to identify how COVID-19 affected the distribution of the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) stage in NSCLC at first diagnosis.
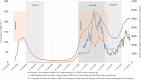
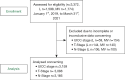
Methods: A retrospective case-control study was conducted, including all patients receiving their first diagnosis of NSCLC in the regions of Leipzig and Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (MV) between January 2019 and March 2021. Patient data were retrieved from the clinical cancer registries of the city of Leipzig and the federal state of MV. Ethical approval for this retrospective evaluation of archived, anonymized patient data was waived by the Scientific Ethical Committee at the Medical Faculty, Leipzig University. Three investigation periods were defined to study the effects of high incidences of SARS-COV-2: the curfew period as an enacted security measure, the period of high incidence rates and the period of the aftermath of high incidences. Differences in the UICC stages between these pandemic periods were studied by Mann-Whitney-U-Test. Pearson's correlation was calculated to examine changes in operability.
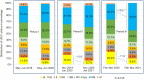
Results: The number of patients diagnosed with NSCLC dropped substantially during investigation periods. There was a significant difference in the UICC status in the aftermath of high incidences and imposed security measures in Leipzig (P=0.016). N-status differed significantly in the aftermath of high incidences and imposed security measures (P=0.022) with a decrease of N0- and an increase of N3-status, respectively, while N1- and N2-status remained relatively unaffected. No pandemic phase showed a significant difference in operability.
Conclusions: The pandemic led to a delay in the diagnosis of NSCLC in the two examined regions. This resulted in higher UICC stages upon diagnosis. However, no increase in inoperable stages was shown. It remains to be seen, how this will affect the overall prognosis of the involved patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); SARS-CoV-2; Union for International Cancer Control stage (UICC stage); securitization.
2023 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-22-1091/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of 7th and 8th editions of the UICC/AJCC TNM staging for non-small cell lung cancer in a non-metastatic North American cohort undergoing primary radiation treatment.Lung Cancer. 2018 Sep;123:116-120. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.06.029. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Lung Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30089581
-
Comparison of the 6th and 7th editions of the AJCC/UICC TNM staging system for gastric cancer focusing on the "N" parameter-related survival: the monoinstitutional NodUs Italian study.World J Surg Oncol. 2015 Jul 16;13:215. doi: 10.1186/s12957-015-0633-3. World J Surg Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26179492 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Levels of Circulating Hsp70 and an Increased Prevalence of CD94+/CD69+ NK Cells Is Predictive for Advanced Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 21;14(22):5701. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225701. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428793 Free PMC article.
-
Efaproxiral: GSJ 61, JP 4, KDD 86, RS 4, RSR 13.Drugs R D. 2005;6(3):178-85. doi: 10.2165/00126839-200506030-00007. Drugs R D. 2005. PMID: 15869322 Review.
-
Staging of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): a review.Respir Med. 2010 Dec;104(12):1767-74. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2010.08.005. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Respir Med. 2010. PMID: 20833010 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and application of a UHPLC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of firmonertinib and its main metabolite AST-5902 in rat plasma: a study on the in vivo drug interaction between firmonertinib and paxlovid.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 12;16:1570206. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1570206. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40421224 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 and lung cancer.Pathologica. 2023 Oct;115(5):284-291. doi: 10.32074/1591-951X-908. Pathologica. 2023. PMID: 38054903 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, et al. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Lyon, 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
