Efficacy and safety of immune checkpoint inhibitors versus chemotherapy in the second-line treatment of advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis and systematic review
- PMID: 37065572
- PMCID: PMC10089833
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-22-1169
Efficacy and safety of immune checkpoint inhibitors versus chemotherapy in the second-line treatment of advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis and systematic review
Abstract
Background: Esophageal cancer (EC) is the seventh most common cancer in the world, with 604,000 new cases diagnosed each year. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) including programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) inhibitors have demonstrated a considerable survival advantage over chemotherapy in numerous randomized controlled trials (RCTs), particularly in patients with advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). In this analysis, we aimed to demonstrate that ICIs are more safe and effective than chemotherapy when used as a second-line treatment for advanced ESCC.
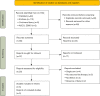
Methods: Publications on the safety and efficiency of ICIs in advanced ESCC that were available prior to February 2022 were searched in the Cochrane Library, Embase, and PubMed databases. Studies with missing data were eliminated, and studies that compared the treatments between the immunotherapy group and chemotherapy group were included. Statistical analysis was carried out using RevMan 5.3, and risk and quality were evaluated with relevant evaluation tools.
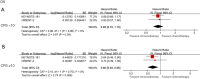
Results: Five studies met the inclusion criteria were selected, involving 1,970 patients with advanced ESCC. We compared chemotherapy and immunotherapy in the second-line treatment of advanced ESCC. ICIs considerably enhanced both the objective response rate (P=0.007) and overall survival (OS; P=0.001). However, the effect of ICIs on progression-free survival (PFS) was not significant (P=0.43). ICIs presented fewer grade 3-5 treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs), and there was also a suggested linkage between both PD-L1 expression and the effectiveness of the therapeutic intervention.
Conclusions: For patients with advanced ESCC, ICIs are more effective and safer than chemotherapy, and thus have a higher treatment value.
Keywords: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC); immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs); meta-analysis.
2023 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-22-1169/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Comment in
-
Immune checkpoint inhibition in advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: how can we personalise management?J Thorac Dis. 2023 Jul 31;15(7):3525-3528. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-598. Epub 2023 Jun 20. J Thorac Dis. 2023. PMID: 37559602 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
