219Three-dimensional printing as a cutting-edge, versatile and personalizable vascular stent manufacturing procedure: Toward tailor-made medical devices
- PMID: 37065659
- PMCID: PMC10090821
- DOI: 10.18063/ijb.v9i2.664
219Three-dimensional printing as a cutting-edge, versatile and personalizable vascular stent manufacturing procedure: Toward tailor-made medical devices
Abstract
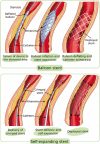
Vascular stents (VS) have revolutionized the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, as evidenced by the fact that the implantation of VS in coronary artery disease (CAD) patients has become a routine, easily approachable surgical intervention for the treatment of stenosed blood vessels. Despite the evolution of VS throughout the years, more efficient approaches are still required to address the medical and scientific challenges, especially when it comes to peripheral artery disease (PAD). In this regard, three-dimensional (3D) printing is envisaged as a promising alternative to upgrade VS by optimizing the shape, dimensions and stent backbone (crucial for optimal mechanical properties), making them customizable for each patient and each stenosed lesion. Moreover, the combination of 3D printing with other methods could also upgrade the final device. This review focuses on the most recent studies using 3D printing techniques to produce VS, both by itself and in combination with other techniques. The final aim is to provide an overview of the possibilities and limitations of 3D printing in the manufacturing of VS. Furthermore, the current situation of CAD and PAD pathologies is also addressed, thus highlighting the main weaknesses of the already existing VS and identifying research gaps, possible market niches and future directions.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Coronary artery disease; Endovascular prosthesis; Peripheral artery disease; Stent; Three-dimensional printing.
Copyright: © 2023, Garcia-Villen, et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures









References
-
- Herrington W, Lacey B, Sherliker P, et al. Epidemiology of atherosclerosis and the potential to reduce the global burden of atherothrombotic disease. Circ Res . 2016;118(4):535–546. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.307611. - PubMed
-
- Song P, Fang Z, Wang H, et al. Global and regional prevalence, burden, and risk factors for carotid atherosclerosis: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and modelling study. Lancet Glob Health . 2020;8(5):e721–e729. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30117-0/ATTACHMENT/B6277D32-2818-4.... - PubMed
-
- WHO World Health Statistics 2020: Monitoring Health for the SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals . 2020 World Health Organization 2020 (WHO)
-
- Poredoš P, Jug B. The prevalence of peripheral arterial disease in high risk subjects and coronary or cerebrovascular patients. Angiology . 2007;58(3):309–315. https://doi.org/10.1177/0003319707302494. - PubMed
-
- Bauersachs R, Zeymer U, Brière JB, et al. Burden of coronary artery disease and peripheral artery disease: A literature review. Cardiovasc Ther . 2019;2019(8295054):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8295054. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
