Urinary complement proteins in IgA nephropathy progression from a relative quantitative proteomic analysis
- PMID: 37065697
- PMCID: PMC10103701
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.15125
Urinary complement proteins in IgA nephropathy progression from a relative quantitative proteomic analysis
Abstract
Aim: IgA nephropathy (IgAN) is one of the leading causes of end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Urine testing is a non-invasive way to track the biomarkers used for measuring renal injury. This study aimed to analyse urinary complement proteins during IgAN progression using quantitative proteomics.
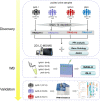
Methods: In the discovery phase, we analysed 22 IgAN patients who were divided into three groups (IgAN 1-3) according to their estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Eight patients with primary membranous nephropathy (pMN) were used as controls. Isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ) labelling, coupled with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, was used to analyse global urinary protein expression. In the validation phase, western blotting and parallel reaction monitoring (PRM) were used to verify the iTRAQ results in an independent cohort (N = 64).
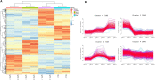
Results: In the discovery phase, 747 proteins were identified in the urine of IgAN and pMN patients. There were different urine protein profiles in IgAN and pMN patients, and the bioinformatics analysis revealed that the complement and coagulation pathways were most activated. We identified a total of 27 urinary complement proteins related to IgAN. The relative abundance of C3, the membrane attack complex (MAC), the complement regulatory proteins of the alternative pathway (AP), and MBL (mannose-binding lectin) and MASP1 (MBL associated serine protease 2) in the lectin pathway (LP) increased during IgAN progression. This was especially true for MAC, which was found to be involved prominently in disease progression. Alpha-N-acetylglucosaminidase (NAGLU) and α-galactosidase A (GLA) were validated by western blot and the results were consistent with the iTRAQ results. Ten proteins were validated in a PRM analysis, and these results were also consistent with the iTRAQ results. Complement factor B (CFB) and complement component C8 alpha chain (C8A) both increased with the progression of IgAN. The combination of CFB and mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1 (MAdCAM-1) also showed potential as a urinary biomarker for monitoring IgAN development.
Conclusion: There were abundant complement components in the urine of IgAN patients, indicating that the activation of AP and LP is involved in IgAN progression. Urinary complement proteins may be used as biomarkers for evaluating IgAN progression in the future.
Keywords: Complement proteins; IgA nephropathy; Proteomics; Urine; α-N-acetylglucosaminidase.
© 2023 Niu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


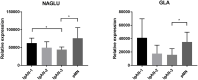


References
-
- Alfakeeh K, Azar M, Alfadhel M, Abdullah AM, Aloudah N, Alsaad KO. Rare genetic variant in the CFB gene presenting as atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome and immune complex diffuse membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, with crescents, successfully treated with eculizumab. Pediatric Nephrology. 2017;32(5):885–891. doi: 10.1007/s00467-016-3577-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ando T, Langley RR, Wang Y, Jordan PA, Minagar A, Alexander JS, Jennings MH. Inflammatory cytokines induce MAdCAM-1 in murine hepatic endothelial cells and mediate alpha-4 beta-7 integrin dependent lymphocyte endothelial adhesion in vitro. BMC Physiology. 2007;7(1):10. doi: 10.1186/1472-6793-7-10. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

