Throat Swab Culture Positivity and Antibiotic Resistance Profiles in Children 2-5 Years of Age Suspected of Bacterial Tonsillitis at Hargeisa Group of Hospitals, Somaliland: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 37065723
- PMCID: PMC10098414
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/6474952
Throat Swab Culture Positivity and Antibiotic Resistance Profiles in Children 2-5 Years of Age Suspected of Bacterial Tonsillitis at Hargeisa Group of Hospitals, Somaliland: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Introduction: Tonsillitis is the third most frequently diagnosed infection in the pediatric age and is associated with significant morbidity and loss of school attendance. Throat swab cultures are useful for the confirmation of children with a clinically suspected tonsillitis. However, Somaliland is one of the underdeveloped countries with a low standard of sanitation and poor health seeking culture. Treatment of tonsillitis with antibiotics is irrational and not empirical. This study determined the bacterial throat swab culture positivity and antibiotic resistance profiles of the bacterial isolates among children 2-5 years of age with suspicion of tonsillitis at Hargeisa Group of Hospital, Somaliland.
Materials and methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted from March to July 2020. A total of 374 children from 2 to 5 years of age suspicion of tonsillitis was included using a convenient sampling method. Throat swabs were collected, and bacterial isolation and identification were done using standard bacteriological procedures. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was done using the disk diffusion method. Data on demographic variables and clinical profiles were collected using structured questionnaires. Logistic regression analysis was computed to identify factors associated with bacterial tonsillitis.
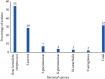
Results: Overall, 120 (32.1%) (95% CI 27.4-36.8%) of children were positive for bacterial throat cultures. Of these, 23 (19.2%) were mixed bacterial isolates. The most frequent bacterial isolates were beta-hemolytic streptococci 78 (55%), Staphylococcus aureus 42 (29%), and Streptococcus pneumoniae 10 (7%). Isolates revealed 83.3-100% rate of resistance to ampicillin. Beta-hemolytic streptococci isolates were 94.9% resistant to ampicillin. S. aureus was resistant to clarithromycin (38%) while S. pneumoniae isolates were 100% resistant to ampicillin. History of tonsillitis (AOR = 0.12; 95% CI = 0.06-0.21), difficulty in swallowing (AOR = 6.99; 95% CI = 3.56-13.73), and attending schools (AOR = 2.98; 95% CI = 1.64-5.42) were found to be associated with positive throat culture.
Conclusions: Resistance to ampicillin and MDR among beta-hemolytic streptococci and other isolates of throat colonizers in children with clinically suspected of bacterial tonsillitis are major concerns in Hargeisa, Somaliland. Therefore, treatments of cases are recommended to be guided by regular culture and antimicrobial susceptibility testing to prevent complications of tonsillitis and associated antibiotic resistance.
Copyright © 2023 Hamda Hussein Darod et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there were no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microbial Composition, Antibiotic Sensitivity Patterns, and Contributing Factors Among Children With Tonsillitis in Hawassa Town, Sidama, Ethiopia.Int J Microbiol. 2025 Apr 16;2025:6366378. doi: 10.1155/ijm/6366378. eCollection 2025. Int J Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40270984 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriological Profiles and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns Among Isolates in Tonsillitis Patients Attending a Tertiary Care Hospital.Cureus. 2024 Oct 25;16(10):e72403. doi: 10.7759/cureus.72403. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39588446 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of urinary tract infection among pregnant women attending Hargeisa Group Hospital, Hargeisa, Somaliland.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 26;12(1):1419. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05452-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35082366 Free PMC article.
-
Peritonsillar abscess: clinical aspects of microbiology, risk factors, and the association with parapharyngeal abscess.Dan Med J. 2017 Mar;64(3):B5333. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28260599 Review.
-
[Tonsillitis and sore throat in childhood].Laryngorhinootologie. 2014 Mar;93 Suppl 1:S84-102. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1363210. Epub 2014 Apr 7. Laryngorhinootologie. 2014. PMID: 24710788 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Throat Swabs- Do They Tell the Entire Story.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025 Feb;77(2):635-638. doi: 10.1007/s12070-024-05028-5. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025. PMID: 40065963
-
Antibiogram Profiling of Antibiotics in Ear, Nose, and Throat Infections in Tertiary Healthcare Settings.Cureus. 2024 Feb 20;16(2):e54587. doi: 10.7759/cureus.54587. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38524079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham Z. S., Bazilio J., Kahinga A. A., Manyahi J., Ntunaguzi D., Massawe E. R. Prevalence and bacteriology of tonsillitis among patients attending otorhinolaryngology Department at Muhimbili National Hospital, Dar es Salaam-Tanzania. Medical Journal of Zambia . 2019;46(1):33–40. doi: 10.55320/mjz.46.1.239. - DOI
-
- Bhardwaj P., Bhalla K., Gupta A., Mehra S., Nehra D., Nanda S. Role of epidemiological risk factors in improving the clinical diagnosis of streptococcal sore throat in pediatric clinical practice. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care . 2019;8(10):3130–3135. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_495_19. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agrawal A., Kumar D., Goyal A., Gupta R., Bhooshan S. Bacteriological evaluation and their antibiotic sensitivity pattern in tonsillitis. IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Science . 2014;13(3):51–55. doi: 10.9790/0853-13355155. - DOI
-
- Rebnord I. K., Sandvik H., Mjelle A. B., Hunskaar S. Factors predicting antibiotic prescription and referral to hospital for children with respiratory symptoms: secondary analysis of a randomised controlled study at out-of-hours services in primary care. BMJ Open . 2017;7(1) doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-012992.e012992 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources