Urinary extracellular vesicles carry valuable hints through mRNA for the understanding of endocrine hypertension
- PMID: 37065732
- PMCID: PMC10096029
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1155011
Urinary extracellular vesicles carry valuable hints through mRNA for the understanding of endocrine hypertension
Abstract
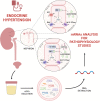
Urinary extracellular vesicles (uEVs), released from cells of the urogenital tract organs, carry precious information about originating tissues. The study of molecules transported through uEVs such as proteins, lipids and nucleic acids provides a deeper understanding of the function of the kidney, an organ involved in the pathogenesis of hypertension and a target of hypertension-mediated organ damage. Molecules derived from uEVs are often proposed for the study of disease pathophysiology or as possible disease diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. Analysis of mRNA loading within uEVs may be a unique and readily obtainable way to assess gene expression patterns of renal cells, otherwise achievable only by an invasive biopsy procedure. Interestingly, the only few studies investigating transcriptomics of hypertension-related genes through the analysis of mRNA from uEVs are inherent to mineralocorticoid hypertension. More specifically, it has been observed that perturbation in human endocrine signalling through mineralcorticoid receptors (MR) activation parallels changes of mRNA transcripts in urine supernatant. Furthermore, an increased copy number of uEVs-extracted mRNA transcripts of the 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 (HSD11B2) gene were detected among subjects affected by apparent mineralocorticoid excess (AME), a hypertension-inducing autosomal recessive disorder due to a defective enzyme function. Moreover, by studying uEVs mRNA, it was observed that the renal sodium chloride cotransporter (NCC) gene expression is modulated under different conditions related to hypertension. Following this perspective, we illustrate here the state of the art and the possible future of uEVs transcriptomics towards a deeper knowledge of hypertension pathophysiology and ultimately more tailored investigational, diagnostic-prognostic approaches.
Keywords: 11-beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2; HSD11B2; endocrine hypertension; exosomes; gene expression; mRNA.
Copyright © 2023 Friso, Castagna, Mango, Olivieri and Pizzolo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Urinary extracellular vesicles as markers to assess kidney sodium transport.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016 Mar;25(2):67-72. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000192. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 26717312 Review.
-
Detection of Urinary Exosomal HSD11B2 mRNA Expression: A Useful Novel Tool for the Diagnostic Approach of Dysfunctional 11β-HSD2-Related Hypertension.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Aug 23;12:681974. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.681974. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34497581 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the DASH diet on the sodium-chloride cotransporter and aquaporin-2 in urinary extracellular vesicles.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024 Jun 1;326(6):F971-F980. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00274.2023. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38634133 Free PMC article.
-
γENaC/CD9 in urinary extracellular vesicles as a potential biomarker of MR activity.J Endocrinol. 2021 Dec 9;252(2):81-90. doi: 10.1530/JOE-21-0228. J Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34755678
-
Exploring the role of urinary extracellular vesicles in kidney physiology, aging, and disease progression.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023 Dec 1;325(6):C1439-C1450. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00349.2023. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37842748 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Urinary exosomes as promising biomarkers for early kidney disease detection.Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2025 Feb 15;13(1):1-19. doi: 10.62347/DAKE5842. eCollection 2025. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2025. PMID: 40124571 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Erdbrügger U, Blijdorp CJ, Bijnsdorp IV, Borràs FE, Burger D, Bussolati B, et al. . Urinary extracellular vesicles: A position paper by the urine task force of the international society for extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles (2021) 10(7):e12093. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12093 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

