Nano-TRAIL: a promising path to cancer therapy
- PMID: 37065863
- PMCID: PMC10099604
- DOI: 10.20517/cdr.2022.82
Nano-TRAIL: a promising path to cancer therapy
Abstract
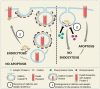
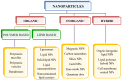
Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand, also called apo-2 ligand (TRAIL/Apo-2L), is a cytokine that triggers apoptosis by binding to TRAIL-R1 (DR4) and TRAIL-R2 (DR5) death receptors. Apoptosis occurs through either the extrinsic or intrinsic pathway. The administration of recombinant human TRAIL (rhTRAIL) or TRAIL-receptor (TRAIL-R) agonists promotes apoptosis preferentially in cancerous cells over normal cells in vitro; this phenomenon has also been observed in clinical studies. The limited efficacy of rhTRAIL in clinical trials could be attributed to drug resistance, short half-life, targeted delivery issues, and off-target toxicities. Nanoparticles are excellent drug and gene delivery systems characterized by improved permeability and retention, increased stability and biocompatibility, and precision targeting. In this review, we discuss resistance mechanisms to TRAIL and methods to overcome TRAIL resistance by using nanoparticle-based formulations developed for the delivery of TRAIL peptides, TRAIL-R agonists, and TRAIL genes to cancer cells. We also discuss combinatorial approaches of chemotherapeutic drugs with TRAIL. These studies demonstrate TRAIL's potential as an anticancer agent.
Keywords: TRAIL; apoptosis; cancer cells; nanomedicine; nanoparticles.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pretreatment with paclitaxel enhances apo-2 ligand/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis of prostate cancer cells by inducing death receptors 4 and 5 protein levels.Cancer Res. 2001 Jan 15;61(2):759-63. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11212279
-
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis in established and primary glioma cell lines.Neurosurg Focus. 2002 Sep 15;13(3):ecp1. doi: 10.3171/foc.2002.13.3.6. Neurosurg Focus. 2002. PMID: 15844877
-
Cotreatment with STI-571 enhances tumor necrosis factor alpha-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL or apo-2L)-induced apoptosis of Bcr-Abl-positive human acute leukemia cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2001 Feb;7(2):350-7. Clin Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11234890
-
Enhancement of therapeutic potential of TRAIL by cancer chemotherapy and irradiation: mechanisms and clinical implications.Drug Resist Updat. 2004 Apr;7(2):139-56. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2004.03.002. Drug Resist Updat. 2004. PMID: 15158769 Review.
-
Should We Keep Walking along the Trail for Pancreatic Cancer Treatment? Revisiting TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand for Anticancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Mar 18;10(3):77. doi: 10.3390/cancers10030077. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29562636 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondria in Cancer Stem Cells: From an Innocent Bystander to a Central Player in Therapy Resistance.Stem Cells Cloning. 2023 Aug 23;16:19-41. doi: 10.2147/SCCAA.S417842. eCollection 2023. Stem Cells Cloning. 2023. PMID: 37641714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the Molecules in EMT: A Potential Therapeutic Opportunity in Breast Cancer.Curr Mol Med. 2025;25(5):567-588. doi: 10.2174/0115665240310780240805114133. Curr Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39162281 Review.
-
Nanoparticle-mediated gene delivery of TRAIL to resistant cancer cells: A review.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 8;10(16):e36057. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36057. eCollection 2024 Aug 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39247341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNA in cervical cancer: Fundamental mechanism and clinical potential.Noncoding RNA Res. 2023 Nov 18;9(1):116-124. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2023.11.009. eCollection 2024 Mar. Noncoding RNA Res. 2023. PMID: 38035041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Turn TRAIL Into Better Anticancer Therapeutic Through TRAIL Fusion Proteins.Cancer Med. 2025 Jan;14(1):e70517. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70517. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 39740038 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
