Effects of reminiscence therapy on psychological outcome among older adults without obvious cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37065888
- PMCID: PMC10098219
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1139700
Effects of reminiscence therapy on psychological outcome among older adults without obvious cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Reminiscence therapy has been a high-benefit and low-cost measure of psychosocial intervention for older adults in recent years. It has attracted much attention in the intervention study of older adults without obvious cognitive impairment. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of reminiscence therapy on psychosocial outcomes among older adults without obvious cognitive impairment and analyze the divergences of different intervention programs (form, duration, and setting) on outcomes.
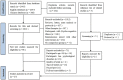
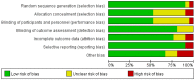
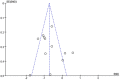
Methods: We searched the commonly used databases and used RevMan 5.4 in the meta-analysis (PROSPERO-ID: CRD42022315237). All eligible trials used the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool and the Effective Public Health Practice Project quality assessment tool to identify the quality and determine the bias risk grade.
Results: Twenty-seven studies were included, involving 1,755 older adults. Meta-analysis showed that reminiscence therapy has a significant effect on both depression and life satisfaction. Group reminiscence played a significant role in improving life satisfaction. Depression symptoms were not affected by the intervention duration (P = 0.06), while life satisfaction was significantly improved after more than 8 weeks of intervention (P < 0.00001). Intervention settings drove differences in depressive symptoms (P = 0.02), and the effect size of the community was larger.
Conclusion: Reminiscence therapy can significantly reduce depressive symptoms and improve life satisfaction. There are different effects of reminiscence therapy in different intervention schemes on psychological outcomes among older adults. More well-designed trials with large sample sizes and long-term follow-ups are necessary to confirm and expand the present results.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=315237, identifier: CRD42022315237.
Keywords: depression; life satisfaction; meta-analysis; older adults; psychosocial outcomes; reminiscence therapy.
Copyright © 2023 Xu, Li, Yan, Ni, Wang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

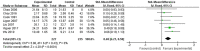
Similar articles
-
The Effectiveness of Reminiscence Therapy on Alleviating Depressive Symptoms in Older Adults: A Systematic Review.Front Psychol. 2021 Aug 17;12:709853. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.709853. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34484066 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of reminiscence therapy interventions for older people: Evidence mapping and qualitative evaluation.J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2023 Jun;30(3):375-388. doi: 10.1111/jpm.12883. Epub 2022 Nov 28. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2023. PMID: 36371647 Review.
-
The effectiveness of reminiscence-based intervention on improving psychological well-being in cognitively intact older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Nurs Stud. 2021 Feb;114:103847. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2020.103847. Epub 2020 Dec 6. Int J Nurs Stud. 2021. PMID: 33352435
-
Psychological interventions to improve self-management of type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Jun;24(28):1-232. doi: 10.3310/hta24280. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32568666 Free PMC article.
-
The Effectiveness of Reminiscence Interventions on Depression and Depressive Symptoms in Community-dwelling Older Adults without Significant Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review.West J Nurs Res. 2025 Jun;47(6):510-523. doi: 10.1177/01939459251324833. Epub 2025 Mar 18. West J Nurs Res. 2025. PMID: 40099342
Cited by
-
The Effect of Reminiscence Therapy on the Assessment of Depression, Anxiety and Self-Esteem in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: An Intervention Study.Int J Older People Nurs. 2025 Jan;20(1):e70004. doi: 10.1111/opn.70004. Int J Older People Nurs. 2025. PMID: 39676577 Free PMC article.
-
Promoting Personalized Reminiscence Among Cognitively Intact Older Adults Through an AI-Driven Interactive Multimodal Photo Album: Development and Usability Study.JMIR Aging. 2024 Jan 23;7:e49415. doi: 10.2196/49415. JMIR Aging. 2024. PMID: 38261365 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness on Quality of Life and Life Satisfaction for Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Life Review and Reminiscence Therapy across Settings.Behav Sci (Basel). 2023 Oct 11;13(10):830. doi: 10.3390/bs13100830. Behav Sci (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37887480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Qualitative Study to Explore the Life Experiences of Older Adults in Oman.Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2023 Oct 3;13(10):2135-2149. doi: 10.3390/ejihpe13100150. Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2023. PMID: 37887151 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of emotion-oriented approaches on psychological outcomes and cognitive function in older adults: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.J Glob Health. 2024 Jun 28;14:04123. doi: 10.7189/jogh.14.04123. J Glob Health. 2024. PMID: 38939961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- United Nations Department Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division . World Population Prospects 2019: Highlights. (2019). Available online at: https://population.un.org/wpp/Publications/Files/WPP2019_Highlights.pdf (accessed October 1, 2022).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

