Comparison of National Dysphagia Diet and International Dysphasia Diet Standardization Initiative Levels for Thickened Drinks Prepared with a Commercial Xanthan Gum-Based Thickener Used for Patients with Dysphagia
- PMID: 37066029
- PMCID: PMC10103603
- DOI: 10.3746/pnf.2023.28.1.83
Comparison of National Dysphagia Diet and International Dysphasia Diet Standardization Initiative Levels for Thickened Drinks Prepared with a Commercial Xanthan Gum-Based Thickener Used for Patients with Dysphagia
Abstract
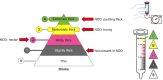
The thickness levels of fluids for patients with dysphagia are established according to the guidelines of the National Dysphagia Diet (NDD) and International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative (IDDSI). The nectar- (level 2), honey- (level 3), and pudding-like (level 4) fluids in NDD are consistent with the mildly (level 2), moderately (level 3), and extremely (level 4) thick fluids in IDDSI, respectively. In this study, NDD levels were compared with IDDSI levels by estimating both the apparent viscosity (ηa,50) and the residual volume (mL) in the IDDSI syringe flow test of thickened drinks prepared with a commercial xanthan gum-based thickener at different concentrations (0.1∼3.1%, w/w). The concentration range of the thickener in thickened drinks at each IDDSI and NDD level increased in the following order: water> orange juice> milk. A small difference was noted in the range of thickener concentration in the same NDD and IDDSI levels for thickened milk when compared with other thickened drinks. These results indicate that the thickener concentration ranges of thickened drinks for the classification of NDD levels differed from those of IDDSI levels, and they appeared to be greatly influenced by the type of drink. These findings could provide useful information for practically indi-cating the reliable thickness levels by the IDDSI flow test in clinical practice.
Keywords: International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative; National Dysphagia Diet; dysphagia; thickened drink.
Copyright © 2023 by The Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
AUTHOR DISCLOSURE STATEMENT The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative study of IDDSI flow test and line-spread test of thickened water prepared with different dysphagia thickeners.J Texture Stud. 2018 Dec;49(6):653-658. doi: 10.1111/jtxs.12360. Epub 2018 Sep 21. J Texture Stud. 2018. PMID: 30187484
-
Standard Recipes for the Preparation of Thickened Barium Liquids Used in the Diagnosis of Dysphagia.Clin Nutr Res. 2019 Oct 25;8(4):265-271. doi: 10.7762/cnr.2019.8.4.265. eCollection 2019 Oct. Clin Nutr Res. 2019. PMID: 31720252 Free PMC article.
-
Flow test by the International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative reveals distinct viscosity parameters of three thickening agents.J Food Sci Technol. 2022 Sep;59(9):3627-3633. doi: 10.1007/s13197-022-05369-5. Epub 2022 Feb 3. J Food Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35875213 Free PMC article.
-
Is IDDSI an Evidence-Based Framework? A Relevant Question for the Frail Older Population.Geriatrics (Basel). 2020 Oct 21;5(4):82. doi: 10.3390/geriatrics5040082. Geriatrics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33096747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modified medication use in dysphagia: the effect of thickener on drug bioavailability-a systematic review.Eur Geriatr Med. 2024 Feb;15(1):19-31. doi: 10.1007/s41999-023-00896-6. Epub 2024 Jan 27. Eur Geriatr Med. 2024. PMID: 38280090 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effect of Setting Time on Viscosity Stability of Xanthan Gum- and Starch-Based Thickened Beverages for Patients with Dysphagia: Comparison of IDDSI Syringe Flow Test and Line-Spread Test.Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2024 Mar 31;29(1):87-92. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2024.29.1.87. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 38576878 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the efficacy of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis drugs in slowing disease progression: A literature review.AIMS Neurosci. 2024 Apr 30;11(2):166-177. doi: 10.3934/Neuroscience.2024010. eCollection 2024. AIMS Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38988889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on digestive disorders following traumatic brain injury.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 20;15:1524495. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1524495. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39759513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Textural Flow Analysis of United States Commercially Available Baby Foods: Packaging and Delivery Method Comparisons by the International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative Framework.Foods. 2025 May 16;14(10):1771. doi: 10.3390/foods14101771. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40428551 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the Polish version of the Functional Oral Intake Scale against flexible endoscopic evaluation of swallowing and the International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative Functional Diet Scale.Front Nutr. 2025 Feb 5;12:1524335. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1524335. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39973923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bolivar-Prados M, Tomsen N, Arenas C, Ibáñez L, Clave P. A bit thick: Hidden risks in thickening products' labelling for dyspha-gia treatment. Food Hydrocolloids. 2022;123:106960. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106960. - DOI
-
- Cichero JA, Lam P, Steele CM, Hanson B, Chen J, Dantas RO, et al. Development of international terminology and definitions for texture-modified foods and thickened fluids used in dysphagia management: the IDDSI framework. Dysphagia. 2017;32:293–314. doi: 10.1007/s00455-016-9758-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
