Transcriptomic data of bevacizumab-adapted colorectal adenocarcinoma cells HCT-116
- PMID: 37066085
- PMCID: PMC10090242
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2023.109069
Transcriptomic data of bevacizumab-adapted colorectal adenocarcinoma cells HCT-116
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Transcriptomic data of Bevacizumab-adapted colorectal adenocarcinoma cells HCT-116" [Data In Brief, Volume 48, (Available online 17 March 2023) 1-9/Article 109069].Data Brief. 2023 Jun 24;49:109343. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2023.109343. eCollection 2023 Aug. Data Brief. 2023. PMID: 37448733 Free PMC article.
Abstract
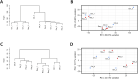
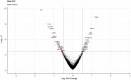
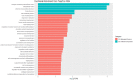
A bioinformatic approach was applied to evaluate the effect of treatment with Bevacizumab on the gene expression profile of colorectal adenocarcinoma cells. The transcriptomic profile of Bevacizumab-adapted HCT-116 (Bev/A) colorectal adenocarcinoma cells was determined and compared with that of the corresponding control cell line by Agilent microarray analysis. Raw data were preprocessed, normalized, filtered, and subjected to a differential expression analysis using standard R/Bioconductor packages (i.e., limma, RankProd). As consequence of Bevacizumab adaptation, 166 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) emerged, most of them (123) resulted downregulated and 43 overexpressed. The list of statistically significant dysregulated genes was used as an input for functional overrepresentation analysis using ToppFun web tool. Such analysis pointed at cell adhesion, cell migration, extracellular matrix organization and angiogenesis as the main dysregulated biological process involved in Bevacizumab-adaptation of HCT116 cells. In addition, gene set enrichment analysis was performed using GSEA, searching for enriched terms within the Hallmarks (H), Canonical Pathways (CP), and Gene Ontology (GO) gene sets. GO terms that showed significant enrichment included: transportome, vascularization, cell adhesion and cytoskeleton, extra cellular matrix (ECM), differentiation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), inflammation and immune response. Raw and normalized microarray data were deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) public repository with accession number GSE221948.
Keywords: Bevacizumab; Bioinformatic analysis; Gene expression; HCT116.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Fan F., Samuel S., Gaur P., Lu J., Dallas N.A., Xia L., Bose D., Ramachandran V., Ellis L.M. Chronic exposure of colorectal cancer cells to bevacizumab promotes compensatory pathways that mediate tumour cell migration. Br. J. Cancer. 2011;104(8):1270–1277. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.81. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lastraioli E., Guasti L., Crociani O., Polvani S., Hofmann G., Witchel H., Bencini L., Calistri M., Messerini L., Scatizzi M., Moretti R., Wanke E., Olivotto M., Mugnai G., Arcangeli A. herg1 gene and HERG1 protein are overexpressed in colorectal cancers and regulate cell invasion of tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64(2):606–611. - PubMed
-
- Breitling R., Armengaud P., Amtmann A., Herzyk P. Rank products: A simple, yet powerful, new method to detect differentially regulated genes in replicated microarray experiments. FEBS Lett. 2004;573:83–92. - PubMed
-
- Hong F., Breitling R., McEntee C.W., Wittner B.S., Nemhauser J.L., Chory J. RankProd: A bioconductor package for detecting differentially expressed genes in meta-analysis. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:2825–2827. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

