Single-cell and long-read sequencing to enhance modelling of splicing and cell-fate determination
- PMID: 37066125
- PMCID: PMC10091034
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.03.023
Single-cell and long-read sequencing to enhance modelling of splicing and cell-fate determination
Abstract
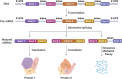
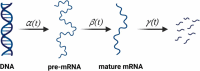
Single-cell sequencing technologies have revolutionised the life sciences and biomedical research. Single-cell sequencing provides high-resolution data on cell heterogeneity, allowing high-fidelity cell type identification, and lineage tracking. Computational algorithms and mathematical models have been developed to make sense of the data, compensate for errors and simulate the biological processes, which has led to breakthroughs in our understanding of cell differentiation, cell-fate determination and tissue cell composition. The development of long-read (a.k.a. third-generation) sequencing technologies has produced powerful tools for investigating alternative splicing, isoform expression (at the RNA level), genome assembly and the detection of complex structural variants (at the DNA level). In this review, we provide an overview of the recent advancements in single-cell and long-read sequencing technologies, with a particular focus on the computational algorithms that help in correcting, analysing, and interpreting the resulting data. Additionally, we review some mathematical models that use single-cell and long-read sequencing data to study cell-fate determination and alternative splicing, respectively. Moreover, we highlight the emerging opportunities in modelling cell-fate determination that result from the combination of single-cell and long-read sequencing technologies.
Keywords: Alternative splicing; Isoform expression; Mathematical modelling; Pesudotemopral trajectory inference; RNA velocity; Transcriptome diversity.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advances in single-cell long-read sequencing technologies.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024 May 20;6(2):lqae047. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqae047. eCollection 2024 Jun. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 38774511 Free PMC article.
-
Methodologies for Transcript Profiling Using Long-Read Technologies.Front Genet. 2020 Jul 7;11:606. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00606. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32733532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Splice Variants and Isoforms in Transcriptomics and Proteomics.Annu Rev Biomed Data Sci. 2023 Aug 10;6:357-376. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biodatasci-020722-044021. Annu Rev Biomed Data Sci. 2023. PMID: 37561601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isoform Age - Splice Isoform Profiling Using Long-Read Technologies.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Aug 2;8:711733. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.711733. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34409069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative splicing in stem cells and development: research progress and emerging technologies.Cell Regen. 2025 Jun 4;14(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s13619-025-00238-w. Cell Regen. 2025. PMID: 40465008 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Applications of single-cell technologies in drug discovery for tumor treatment.iScience. 2024 Jul 10;27(8):110486. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110486. eCollection 2024 Aug 16. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39171294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Role of Gut Bacteriome Dysbiosis as a Leading Cause of Periprosthetic Infection: A Comprehensive Literature Review.Microorganisms. 2023 Jul 9;11(7):1778. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11071778. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37512950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in single-cell long-read sequencing technologies.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024 May 20;6(2):lqae047. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqae047. eCollection 2024 Jun. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 38774511 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of prion proteins in mammalian development.Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2024 Dec 10;28(1):551-566. doi: 10.1080/19768354.2024.2436860. eCollection 2024. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2024. PMID: 39664939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting RNA splicing modulation: new perspectives for anticancer strategy?J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Jan 30;44(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03279-w. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39885614 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tang F., Barbacioru C., Wang Y., Nordman E., Lee C., Xu N., et al. mRNA-Seq whole-transcriptome analysis of a single cell. Nat Methods. 2009;6:377–382. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
