This is a preprint.
Multicellular, IVT-derived, unmodified human transcriptome for nanopore-direct RNA analysis
- PMID: 37066160
- PMCID: PMC10104151
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.04.06.535889
Multicellular, IVT-derived, unmodified human transcriptome for nanopore-direct RNA analysis
Update in
-
Multicellular, IVT-derived, unmodified human transcriptome for nanopore-direct RNA analysis.GigaByte. 2024 Jun 17;2024:gigabyte129. doi: 10.46471/gigabyte.129. eCollection 2024. GigaByte. 2024. PMID: 38962390 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Nanopore direct RNA sequencing (DRS) enables measurements of RNA modifications. Modification-free transcripts are a practical and targeted control for DRS, providing a baseline measurement for canonical nucleotides within a matched and biologically derived sequence context. However, these controls can be challenging to generate and carry nanopore-specific nuances that can impact analysis. We produced DRS datasets using modification-free transcripts from in vitro transcription (IVT) of cDNA from six immortalized human cell lines. We characterized variation across cell lines and demonstrated how these may be interpreted. These data will serve as a versatile control and resource to the community for RNA modification analysis of human transcripts.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTEREST STATEMENT The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
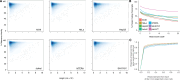

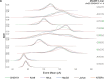
References
-
- Nguyen TA, Heng JWJ, Kaewsapsak P, Kok EPL, Stanojević D, Liu H, et al.. Direct identification of A-to-I editing sites with nanopore native RNA sequencing. Nat Methods. 19:833–442022; - PubMed
-
- Boccaletto P, Bagiński B. MODOMICS: An Operational Guide to the Use of the RNA Modification Pathways Database. In: Picardi E, editor. RNA Bioinformatics. New York, NY: Springer US; p. 481–505. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
