Analysis of biomechanical characterization of the thumb rubbing method
- PMID: 37066946
- PMCID: PMC10200190
- DOI: 10.3233/THC-236044
Analysis of biomechanical characterization of the thumb rubbing method
Abstract
Background: Thumb rubbing is one of the widely accepted massage techniques, owing to its simple and effective operation. Exploring the biomechanical characteristics of the thumb rubbing method can assist the understanding of the operating characteristics of manipulation, thereby improvising the therapeutic role of manipulation.
Objective: To study the kinematic and kinetic characteristics of the thumb kneading method from the biomechanical point of view, and to quantitatively analyze the key points of thumb kneading operation.
Methods: We explored the biomechanical characteristics of the thumb kneading operation by an analysis of the parameters scored by the experts and students using the "thumb kneading data glove and data collection system".
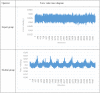
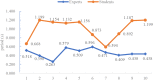
Results: (1) Force trajectory: The expert group showed a regular force trajectory compared to the student group, with a stable thumb suction position, small drift and concentrated force. (2) Force value: The average force value of the expert group was concentrated in the range 0.614 ± 0.041 kg, while the average force value of the student group was concentrated in the range 0.650 ± 0.146 kg and the difference was not statistically significant. (3) Frequency: The frequency of the expert group was mainly concentrated in the range 134.280 ± 39.106 times/min, while that of the student group was 66.04 ± 23.651 times/min, (P< 0.05). (4) Period: The operation cycle during the thumb kneading of the expert and student groups was mainly concentrated in the range of 0.476 ± 0.117 s and (0.990 ± 0.259) s, respectively, and the difference was statistically significant (P< 0.05).
Conclusion: The present study revealed that the technical operation of the expert group was more stable and standardized than that of the student group. It was found that the force value was inversely proportional to the frequency of the operation. In the "circular rotation" operation of the thumb rubbing method, the force value conversion degree of different parts of the thumb reflected the motion trajectory. Furthermore, the "circular rotation" operation performed by the expert group was better than the student group. The study of the parameters, including the angle of frequency, period and force value can reflect the biomechanical characteristics of thumb rubbing method to a significant extent.
Keywords: biomechanics; mechanical characteristics; thumb rubbing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Weerapong P, Hume PA, Kolt GS. The mechanisms of massage and effects on performance, muscle recovery and injury prevention. Sports Medicine. 2005; 35(3): 235-256. - PubMed
-
- Fang L, Fang M. Research progress on the standardization of Chinese Tuina therapy: A short review. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine. 2013; 19(1): 68-72. - PubMed
-
- Zhou X, Zhu QG, Kong LJ et al. Modern methods to improve the quality of scientific research on traditional Chinese massagechina. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy. 2021; 36(8): 4785-4788.
-
- Wang GC Bi YS, Zhang SF et al. Determination and application of dynamic curve of massage technique. Journal of Shandong Collece of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 1982(1): 72-76. doi: 10.16294/j.cnki.1007-659x.1982.01.017. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources