Multi-shell connectome DWI-based graph theory measures for the prediction of temporal lobe epilepsy and cognition
- PMID: 37067514
- PMCID: PMC10267614
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhad098
Multi-shell connectome DWI-based graph theory measures for the prediction of temporal lobe epilepsy and cognition
Abstract
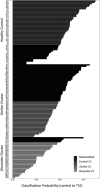
Temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) is the most common epilepsy syndrome that empirically represents a network disorder, which makes graph theory (GT) a practical approach to understand it. Multi-shell diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) was obtained from 89 TLE and 50 controls. GT measures extracted from harmonized DWI matrices were used as factors in a support vector machine (SVM) analysis to discriminate between groups, and in a k-means algorithm to find intrinsic structural phenotypes within TLE. SVM was able to predict group membership (mean accuracy = 0.70, area under the curve (AUC) = 0.747, Brier score (BS) = 0.264) using 10-fold cross-validation. In addition, k-means clustering identified 2 TLE clusters: 1 similar to controls, and 1 dissimilar. Clusters were significantly different in their distribution of cognitive phenotypes, with the Dissimilar cluster containing the majority of TLE with cognitive impairment (χ2 = 6.641, P = 0.036). In addition, cluster membership showed significant correlations between GT measures and clinical variables. Given that SVM classification seemed driven by the Dissimilar cluster, SVM analysis was repeated to classify Dissimilar versus Similar + Controls with a mean accuracy of 0.91 (AUC = 0.957, BS = 0.189). Altogether, the pattern of results shows that GT measures based on connectome DWI could be significant factors in the search for clinical and neurobehavioral biomarkers in TLE.
Keywords: SVM; TLE; connectome DWI; graph theory; k-means phenotypes.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures




References
-
- Ades-Aron B, Veraart J, Kochunov P, McGuire S, Sherman P, Kellner E, Novikov DS, Fieremans E. Evaluation of the accuracy and precision of the diffusion parameter EStImation with Gibbs and NoisE removal pipeline. NeuroImage. 2018 Dec:183:532–543. 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.07.066. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arnold TC, Muthukrishnan R, Pattnaik AR, Sinha N, Gibson A, Gonzalez H, das S, Litt B, Englot DJ, Morgan VL, et al. Deep learning-based automated segmentation of resection cavities on postsurgical epilepsy MRI. Neuroimage Clin. 2022:36:103154. 10.1016/j.nicl.2022.103154. Epub 2022 Aug 17. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

