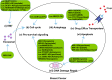
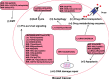
Landscape of NcRNAs involved in drug resistance of breast cancer
- PMID: 37067729
- PMCID: PMC10250522
- DOI: 10.1007/s12094-023-03189-3
Landscape of NcRNAs involved in drug resistance of breast cancer
Abstract
Breast cancer (BC) leads to the most amounts of deaths among women. Chemo-, endocrine-, and targeted therapies are the mainstay drug treatments for BC in the clinic. However, drug resistance is a major obstacle for BC patients, and it leads to poor prognosis. Accumulating evidences suggested that noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) are intricately linked to a wide range of pathological processes, including drug resistance. Till date, the correlation between drug resistance and ncRNAs is not completely understood in BC. Herein, we comprehensively summarized a dysregulated ncRNAs landscape that promotes or inhibits drug resistance in chemo-, endocrine-, and targeted BC therapies. Our review will pave way for the effective management of drug resistance by targeting oncogenic ncRNAs, which, in turn will promote drug sensitivity of BC in the future.
Keywords: ASOs; Breast cancer; Chemotherapy; Endocrine therapy; NcRNAs; Resistance; Targeted therapy.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of endocrine resistance in breast cancer: an overview of the proposed roles of noncoding RNA.Breast Cancer Res. 2015 Mar 17;17:40. doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0542-y. Breast Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25849966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs and their role in breast cancer pathogenesis and drug resistance: Navigating the non-coding landscape review.Exp Cell Res. 2025 Jan 15;444(2):114365. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.114365. Epub 2024 Dec 1. Exp Cell Res. 2025. PMID: 39626864 Review.
-
Roles of noncoding RNAs in drug resistance in multiple myeloma.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Nov;235(11):7681-7695. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29726. Epub 2020 Apr 23. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32324301 Review.
-
Competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) cross talk and language in ceRNA regulatory networks: A new look at hallmarks of breast cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jul;234(7):10080-10100. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27941. Epub 2018 Dec 10. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30537129 Review.
-
ncRNA-mediated ceRNA regulatory network: Transcriptomic insights into breast cancer progression and treatment strategies.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jun;162:114698. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114698. Epub 2023 Apr 13. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37060661 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-coding RNAs in breast cancer: with a focus on glucose metabolism reprogramming.Discov Oncol. 2023 May 19;14(1):72. doi: 10.1007/s12672-023-00687-2. Discov Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37204526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
lncRNA-microRNA axis in cancer drug resistance: particular focus on signaling pathways.Med Oncol. 2024 Jan 9;41(2):52. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02263-8. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38195957 Review.
-
Exploring the molecular landscape of osteosarcoma through PTTG family genes using a detailed multi-level methodology.Front Genet. 2024 Jul 30;15:1431668. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1431668. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39139816 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Non-coding RNAs in breast cancer, volume II.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 11;15:1561190. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1561190. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40008003 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Amelio I., Bernassola F., Candi E., Emerging roles of long non-coding RNAs in breast cancer biology and management, Semin Cancer Biol. (2020). - PubMed
-
- Perez EA, Romond EH, Suman VJ, Jeong JH, Sledge G, Geyer CE, Martino S, Rastogi P, Gralow J, Swain SM, Winer EP, Colon-Otero G, Davidson NE, Mamounas E, Zujewski JA, Wolmark N. Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer: planned joint analysis of overall survival from NSABP B-31 and NCCTG N9831. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(32):3744–52. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.55.5730. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical