Comparative genomic analysis of Halomonas campaniensis wild-type and ultraviolet radiation-mutated strains reveal genomic differences associated with increased ectoine production
- PMID: 37067733
- PMCID: PMC10622362
- DOI: 10.1007/s10123-023-00356-y
Comparative genomic analysis of Halomonas campaniensis wild-type and ultraviolet radiation-mutated strains reveal genomic differences associated with increased ectoine production
Abstract
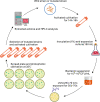
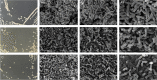
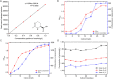
Ectoine is a natural amino acid derivative and one of the most widely used compatible solutes produced by Halomonas species that affects both cellular growth and osmotic equilibrium. The positive effects of UV mutagenesis on both biomass and ectoine content production in ectoine-producing strains have yet to be reported. In this study, the wild-type H. campaniensis strain XH26 (CCTCCM2019776) was subjected to UV mutagenesis to increase ectoine production. Eight rounds of mutagenesis were used to generate mutated XH26 strains with different UV-irradiation exposure times. Ectoine extract concentrations were then evaluated among all strains using high-performance liquid chromatography analysis, alongside whole genome sequencing with the PacBio RS II platform and comparison of the wild-type strain XH26 and the mutant strain G8-52 genomes. The mutant strain G8-52 (CCTCCM2019777) exhibited the highest cell growth rate and ectoine yields among mutated strains in comparison with strain XH26. Further, ectoine levels in the aforementioned strain significantly increased to 1.51 ± 0.01 g L-1 (0.65 g g-1 of cell dry weight), representing a twofold increase compared to wild-type cells (0.51 ± 0.01 g L-1) when grown in culture medium for ectoine accumulation. Concomitantly, electron microscopy revealed that mutated strain G8-52 cells were obviously shorter than wild-type strain XH26 cells. Moreover, strain G8-52 produced a relatively stable ectoine yield (1.50 g L-1) after 40 days of continuous subculture. Comparative genomics analysis suggested that strain XH26 harbored 24 mutations, including 10 nucleotide insertions, 10 nucleotide deletions, and unique single nucleotide polymorphisms. Notably, the genes orf00723 and orf02403 (lipA) of the wild-type strain mutated to davT and gabD in strain G8-52 that encoded for 4-aminobutyrate-2-oxoglutarate transaminase and NAD-dependent succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, respectively. Consequently, these genes may be involved in increased ectoine yields. These results suggest that continuous multiple rounds of UV mutation represent a successful strategy for increasing ectoine production, and that the mutant strain G8-52 is suitable for large-scale fermentation applications.
Keywords: Ectoine; Ectoine producer; Ectoine yield; Genomic analysis; Halomonas; UV mutagenesis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of ABC transporters negatively correlates with ectoine biosynthesis in Halomonas campaniensis under NaCl and ultraviolet mutagenesis treatments revealed by transcriptomic and proteomics combined analysis.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 20;25(1):1114. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-11003-9. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39567869 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic engineering of Halomonas campaniensis strain XH26 to remove competing pathways to enhance ectoine production.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 15;13(1):9732. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36975-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37322079 Free PMC article.
-
Study of osmoadaptation mechanisms of halophilic Halomonas alkaliphila XH26 under salt stress by transcriptome and ectoine analysis.Extremophiles. 2022 Mar 1;26(1):14. doi: 10.1007/s00792-022-01256-1. Extremophiles. 2022. PMID: 35229247
-
Microbial production of ectoine and hydroxyectoine as high-value chemicals.Microb Cell Fact. 2021 Mar 26;20(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12934-021-01567-6. Microb Cell Fact. 2021. PMID: 33771157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Advances in the microbial production of the compatible solute ectoine: a review].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2022 Mar 25;38(3):868-881. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.210368. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35355460 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Expression of ABC transporters negatively correlates with ectoine biosynthesis in Halomonas campaniensis under NaCl and ultraviolet mutagenesis treatments revealed by transcriptomic and proteomics combined analysis.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 20;25(1):1114. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-11003-9. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39567869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Azarbaijani R, Yeganeh LP, Blom J, Younesi H, Fazeli SAS, et al. Comparative genome analysis of Oceanimonas sp. GK1, a halotolerant bacterium with considerable xenobiotics degradation potentials. Ann Microbiol. 2015;66(2):703–716. doi: 10.1007/s13213-015-1156-4. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

