ADP enhances the allosteric activation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase by calmodulin
- PMID: 37068230
- PMCID: PMC10151598
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2300902120
ADP enhances the allosteric activation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase by calmodulin
Abstract
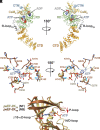
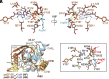
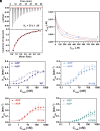
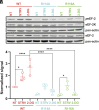
Protein translation, one of the most energy-consumptive processes in a eukaryotic cell, requires robust regulation, especially under energy-deprived conditions. A critical component of this regulation is the suppression of translational elongation through reduced ribosome association of the GTPase eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (eEF-2) resulting from its specific phosphorylation by the calmodulin (CaM)-activated α-kinase eEF-2 kinase (eEF-2K). It has been suggested that the eEF-2K response to reduced cellular energy levels is indirect and mediated by the universal energy sensor AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) through direct stimulatory phosphorylation and/or downregulation of the eEF-2K-inhibitory nutrient-sensing mTOR pathway. Here, we provide structural, biochemical, and cell-biological evidence of a direct energy-sensing role of eEF-2K through its stimulation by ADP. A crystal structure of the nucleotide-bound complex between CaM and the functional core of eEF-2K phosphorylated at its primary stimulatory site (T348) reveals ADP bound at a unique pocket located on the face opposite that housing the kinase active site. Within this basic pocket (BP), created at the CaM/eEF-2K interface upon complex formation, ADP is stabilized through numerous interactions with both interacting partners. Biochemical analyses using wild-type eEF-2K and specific BP mutants indicate that ADP stabilizes CaM within the active complex, increasing the sensitivity of the kinase to CaM. Induction of energy stress through glycolysis inhibition results in significantly reduced enhancement of phosphorylated eEF-2 levels in cells expressing ADP-binding compromised BP mutants compared to cells expressing wild-type eEF-2K. These results suggest a direct energy-sensing role for eEF-2K through its cooperative interaction with CaM and ADP.
Keywords: alpha-kinase; calmodulin; protein translation; serine/threonine kinase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Revealing eEF-2 kinase: recent structural insights into function.Trends Biochem Sci. 2024 Feb;49(2):169-182. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2023.11.004. Epub 2023 Dec 16. Trends Biochem Sci. 2024. PMID: 38103971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signal Integration at Elongation Factor 2 Kinase: THE ROLES OF CALCIUM, CALMODULIN, AND SER-500 PHOSPHORYLATION.J Biol Chem. 2017 Feb 3;292(5):2032-2045. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.753277. Epub 2016 Dec 12. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 27956550 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Dynamics of the Activation of Elongation Factor 2 Kinase by Ca2+-Calmodulin.J Mol Biol. 2018 Aug 17;430(17):2802-2821. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.05.033. Epub 2018 May 22. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29800565 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the complex between calmodulin and a functional construct of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase bound to an ATP-competitive inhibitor.J Biol Chem. 2023 Jun;299(6):104813. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104813. Epub 2023 May 11. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37172726 Free PMC article.
-
What is the impact of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase on cancer: A systematic review.Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Aug 15;857:172470. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172470. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31226250
Cited by
-
The Critical Role of the C-terminal Lobe of Calmodulin in Activating Eukaryotic Elongation Factor 2 Kinase.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 16:2025.05.13.653565. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.13.653565. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40462953 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Revealing eEF-2 kinase: recent structural insights into function.Trends Biochem Sci. 2024 Feb;49(2):169-182. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2023.11.004. Epub 2023 Dec 16. Trends Biochem Sci. 2024. PMID: 38103971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ser500 phosphorylation acts as a conformational switch to prime eEF-2K for activation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 1:2025.06.30.662482. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.30.662482. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40631149 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
In-Silico Screening-Based Discovery of New Natural eEF2K Inhibitors with Neuritogenic Activity.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2025 Mar 4;16(3):475-482. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.4c00635. eCollection 2025 Mar 13. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2025. PMID: 40104800
-
Architecture and activation of human muscle phosphorylase kinase.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 28;15(1):2719. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47049-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38548794 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

