High-Contrast PET Imaging with [18F]NT160, a Class-IIa Histone Deacetylase Probe for In Vivo Imaging of Epigenetic Machinery in the Central Nervous System
- PMID: 37068265
- PMCID: PMC10150721
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c02064
High-Contrast PET Imaging with [18F]NT160, a Class-IIa Histone Deacetylase Probe for In Vivo Imaging of Epigenetic Machinery in the Central Nervous System
Abstract
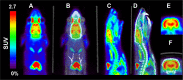
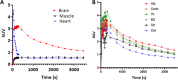
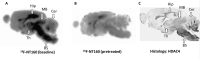
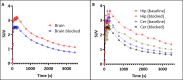
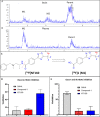
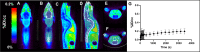
We utilized positron emission tomography (PET) imaging in vivo to map the spatiotemporal biodistribution/expression of class-IIa histone deacetylases (class-IIa HDACs) in the central nervous system (CNS). Herein we report an improved radiosynthesis of [18F]NT160 using 4-hydroxy-TEMPO which led to a significant improvement in radiochemical yield and molar activity. PET imaging with [18F]NT160, a highly potent class-IIa HDAC inhibitor, led to high-quality and high-contrast images of the brain. [18F]NT160 displayed excellent pharmacokinetic and imaging characteristics: brain uptake is high in gray matter regions, tissue kinetics are appropriate for a 18F-tracer, and specific binding for class-IIa HDACs is demonstrated by self-blockade. Higher uptake with [18F]NT160 was observed in the hippocampus, thalamus, and cortex while the uptake in the cerebellum was relatively low. Overall, our current studies with [18F]NT160 will likely facilitate the development and clinical translation of PET tracers for imaging of class-IIa HDACs biodistribution/expression in cancer and the CNS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
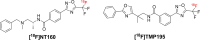


Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis, biochemical evaluation, radiolabeling and in vivo imaging with high affinity class-IIa histone deacetylase inhibitor for molecular imaging and targeted therapy.Eur J Med Chem. 2022 Jan 15;228:114011. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.114011. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Eur J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34875522 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Histone Deacetylase Class IIa Selective Substrate Radiotracers for PET Imaging of Epigenetic Regulation in the Brain.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 5;10(8):e0133512. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133512. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26244761 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular imaging HDACs class IIa expression-activity and pharmacologic inhibition in intracerebral glioma models in rats using PET/CT/(MRI) with [18F]TFAHA.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 5;9(1):3595. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40054-2. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30837601 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the Development of PET Ligands Targeting Histone Deacetylases for the Assessment of Neurodegenerative Diseases.Molecules. 2018 Jan 31;23(2):300. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020300. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29385079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Class IIa HDACs: Insights from Phenotypes and Inhibitors.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(42):8628-8672. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666210629160647. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34212828 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Radiopharmaceuticals: A "Hot" Topic.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023 Dec 18;7(1):1-7. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.3c00347. eCollection 2024 Jan 12. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 38230278 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Design and radiosynthesis of class-IIa HDAC inhibitor with high molar activity via repositioning the 18F-radiolabel.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 2;14(1):15100. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65668-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38956204 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Radiolabeled Cyclin-Dependent Kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) Inhibitor for Brain and Cancer PET Imaging.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 22;25(13):6870. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136870. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38999983 Free PMC article.
-
Demystifying the Role of Neuroinflammatory Mediators as Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease: A Review.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Sep 26;7(10):2987-3003. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00457. eCollection 2024 Oct 11. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39416969 Review.
References
-
- Faraco G.; Pancani T.; Formentini L.; Mascagni P.; Fossati G.; Leoni F.; Moroni F.; Chiarugi A. Pharmacological inhibition of histone deacetylases by suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid specifically alters gene expression and reduces ischemic injury in the mouse brain. Molecular pharmacology 2006, 70 (6), 1876–1884. 10.1124/mol.106.027912. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ren M.; Leng Y.; Jeong M.; Leeds P. R.; Chuang D. M. Valproic acid reduces brain damage induced by transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats: potential roles of histone deacetylase inhibition and heat shock protein induction. Journal of neurochemistry 2004, 89 (6), 1358–1367. 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02406.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kim H. J.; Rowe M.; Ren M.; Hong J. S.; Chen P. S.; Chuang D. M. Histone deacetylase inhibitors exhibit anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects in a rat permanent ischemic model of stroke: multiple mechanisms of action. J. Pharmacol Exp Ther 2007, 321 (3), 892–901. 10.1124/jpet.107.120188. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

