Identification of pyrrolo[3',4':3,4]cyclohepta[1,2-d][1,2]oxazoles as promising new candidates for the treatment of lymphomas
- PMID: 37068384
- PMCID: PMC10287037
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115372
Identification of pyrrolo[3',4':3,4]cyclohepta[1,2-d][1,2]oxazoles as promising new candidates for the treatment of lymphomas
Abstract
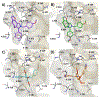
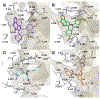
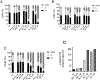
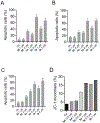
Unsatisfactory outcomes for relapsed/refractory lymphoma patients prompt continuing efforts to develop new therapeutic strategies. Our previous studies on pyrrole-based anti-lymphoma agents led us to synthesize a new series of twenty-six pyrrolo[3',4':3,4]cyclohepta[1,2-d] [1,2]oxazole derivatives and study their antiproliferative effects against a panel of four non-Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines. Several candidates showed significant anti-proliferative effects, with IC50's reaching the sub-micromolar range in at least one cell line, with compound 3z demonstrating sub-micromolar growth inhibitory effects towards the entire panel. The VL51 cell line was the most sensitive, with an IC50 value of 0.10 μM for 3z. Our earlier studies had shown that tubulin was a prominent target of many of our oxazole derivatives. We therefore examined their effects on tubulin assembly and colchicine binding. While 3u and 3z did not appear to target tubulin, good activity was observed with 3d and 3p. Molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations allowed us to rationalize the binding mode of the synthesized compounds toward tubulin. All ligands exhibited a better affinity for the colchicine site, confirming their specificity for this binding pocket. In particular, a better affinity and free energy of binding was observed for 3d and 3p. This result was confirmed by experimental data, indicating that, although both 3d and 3p significantly affected tubulin assembly, only 3d showed activity comparable to that of combretastatin A-4, while 3p was about 4-fold less active. Cell cycle analysis showed that compounds 3u and especially 3z induced a block in G2/M, a strong decrease in S phase even at low compound concentrations and apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway. Thus, the mechanism of action of 3u and 3z remains to be elucidated. Very high selectivity toward cancer cells and low toxicity in human peripheral blood lymphocytes were observed, highlighting the good potential of these agents in cancer therapy and encouraging further exploration of this compound class to obtain new small molecules as effective lymphoma treatments.
Keywords: Antitumor agents; Hematological malignancies; Isoxazoles; Lymphoma; pyrrolo[3′,4’:3,4]cyclohepta[1,2-d][1,2]oxazoles.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Francesco Bertoni reports financial support was provided by ADC Therapeutics, Bayer AG, Cellestia, Helsinn, HTG Molecular Diagnostics, ImmunoGen, Menarini Ricerche, NEOMED Therapeutics 1, Nordic Nanovector ASA, Helsinn, Menarini. Eugenio Gaudio reports a relationship with Helsinn Healthcare SA that includes: employment.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pyrrolo[2',3':3,4]cyclohepta[1,2-d][1,2]oxazoles, a New Class of Antimitotic Agents Active against Multiple Malignant Cell Types.J Med Chem. 2020 Oct 22;63(20):12023-12042. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01315. Epub 2020 Oct 11. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32986419 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of new quinolines as potent colchicine binding site inhibitors: design, synthesis, docking studies, and anti-proliferative evaluation.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021 Dec;36(1):640-658. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2021.1883598. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33588683 Free PMC article.
-
Design and discovery of new antiproliferative 1,2,4-triazin-3(2H)-ones as tubulin polymerization inhibitors targeting colchicine binding site.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Jul;112:104965. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104965. Epub 2021 May 5. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 34020238
-
Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of 5-phenyloxazole-2-carboxylic acid derivatives as novel inhibitors of tubulin polymerization.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021 May 15;40:127968. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.127968. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021. PMID: 33753264
-
Discovery of N-benzylarylamide derivatives as novel tubulin polymerization inhibitors capable of activating the Hippo pathway.Eur J Med Chem. 2022 Oct 5;240:114583. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114583. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Eur J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35834904
Cited by
-
Benzimidazoles Containing Piperazine Skeleton at C-2 Position as Promising Tubulin Modulators with Anthelmintic and Antineoplastic Activity.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Oct 25;16(11):1518. doi: 10.3390/ph16111518. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004384 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing Study of 4-Acyl-1-phenylaminocarbonyl-2-substituted-piperazine Derivatives as Potential Anticancer Agents-In Vitro Evaluation against Breast Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 1;24(23):17041. doi: 10.3390/ijms242317041. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069364 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer potential and structure activity studies of purine and pyrimidine derivatives: an updated review.Mol Divers. 2025 Feb;29(1):817-848. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-10870-4. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 38856835 Review.
-
Synthesis of 1-(2-Hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)-5-oxopyrrolidine-3-carboxylic Acid Derivatives as a Promising Scaffold Against Disease-Causing Bacteria Relevant to Public Health.Molecules. 2025 Jun 18;30(12):2639. doi: 10.3390/molecules30122639. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40572602 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Antitumor Activity of Xanthones Conjugated with Amino Acids.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 9;25(4):2121. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042121. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396802 Free PMC article.
References
-
- PDQ Adult Treatment Editorial Board. Adult Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatment (PDQ®): Health Professional Version. 2022. Jul 6. In: PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet] Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute (US); 2002, 2002.
-
- PDQ Adult Treatment Editorial Board. Adult Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatment (PDQ®): Health Professional Version. 2022. Jul 15. In: PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet] Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute (US); 2002, 2002.
-
- Yang J, Liu Y, Lan S, Yu S, Luo D, Shan H, Zhong X, Yan G, Li R, Discovery of 2‑Methyl-2-(4-(2-methyl-8-(1H‑pyrrolo[2,3‑b]pyridin-6-yl)‑1H‑naphtho[1,2‑d]imidazol-1-yl)phenyl)propanenitrile as a Novel PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor with Enhanced Antitumor Efficacy In Vitro and In Vivo, J. Med. Chem 65 (2022) 12781–12801. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00572. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

