The effect of silencing the Tip60 gene on the response to radiotherapy in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 37069013
- PMCID: PMC10300608
- DOI: 10.1016/j.breast.2023.04.001
The effect of silencing the Tip60 gene on the response to radiotherapy in breast cancer cells
Abstract
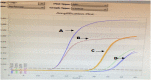
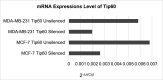
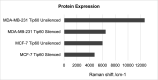
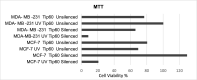
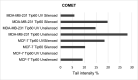
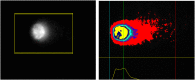
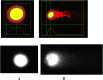
Since patients with triple-negative breast cancer do not respond to hormone therapy, the main treatment method is the combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Because the DNA of the tumor cell is the target in both some chemotherapeutics and radiotherapy, problems may occur in individuals with a high DNA repair pathway. It is suggested that high expression of the Tip60 gene, which has an important role in repairing DNA damage, will increase the repair of DNA double-strand breaks in tumor cells, especially during radiotherapy treatment, thus reducing the response to treatment and adversely affecting treatment. In this study, for the first time, the role of the silenced and active Tip60 gene in response to radiotherapy in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells was investigated. For this purpose, the Tip60 gene was silenced by applying siRNA to the cell lines and UV was applied. In the study, cytotoxicity and DNA breaks were measured by MTT and COMET methods, and mRNA and protein expression values were measured by PCR and Raman spectrophotometer in silenced, unsilenced, UV-treated, and non-UV-treated cell lines. According to the results of the study, increased DNA damage was observed in MCF-7 cell lines in which the Tip60 gene was silenced, and radiotherapy was applied, compared to the cell lines with the Tip60 gene active. It was observed that DNA damage in MDA-MB-231 cell lines was less than in cell lines with the active Tip60 gene.
Keywords: Comet; MCF-7; MDA-MB-231; MTT; PCR; Protein expression; Tip60; siRNA.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicial to the impartiality of the reported research.
Figures
References
-
- Kang H.S., et al. Diffusion kurtosis MR imaging of invasive breast cancer: correlations with prognostic factors and molecular subtypes. J Magn Reson Imag. 2022;56(1):110–120. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

