Accuracy of a smartphone application for blood pressure estimation in Bangladesh, South Africa, and Tanzania
- PMID: 37069209
- PMCID: PMC10107587
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-023-00804-z
Accuracy of a smartphone application for blood pressure estimation in Bangladesh, South Africa, and Tanzania
Abstract
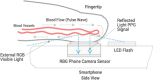
Undetected and unmonitored hypertension carries substantial mortality and morbidity, especially during pregnancy. We assessed the accuracy of OptiBPTM, a smartphone application for estimating blood pressure (BP), across diverse settings. The study was conducted in community settings: Gaibandha, Bangladesh and Ifakara, Tanzania for general populations, and Kalafong Provincial Tertiary Hospital, South Africa for pregnant populations. Based on guidance from the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 81,060-2:2018 for non-invasive BP devices and global consensus statement, we compared BP measurements taken by two independent trained nurses on a standard auscultatory cuff to the BP measurements taken by a research version of OptiBPTM called CamBP. For ISO criterion 1, the mean error was 0.5 ± 5.8 mm Hg for the systolic blood pressure (SBP) and 0.1 ± 3.9 mmHg for the diastolic blood pressure (DBP) in South Africa; 0.8 ± 7.0 mmHg for the SBP and -0.4 ± 4.0 mmHg for the DBP in Tanzania; 3.3 ± 7.4 mmHg for the SBP and -0.4 ± 4.3 mmHg for the DBP in Bangladesh. For ISO criterion 2, the average standard deviation of the mean error per subject was 4.9 mmHg for the SBP and 3.4 mmHg for the DBP in South Africa; 6.3 mmHg for the SBP and 3.6 mmHg for the DBP in Tanzania; 6.4 mmHg for the SBP and 3.8 mmHg for the DBP in Bangladesh. OptiBPTM demonstrated accuracy against ISO standards in study populations, including pregnant populations, except in Bangladesh for SBP (criterion 2). Further research is needed to improve performance across different populations and integration within health systems.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation Client Services. Making the World a Healthier Place for Mothers: Trends and Opportunities for Action in Maternal Health. (IHME, 2019).
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Recommendations for Prevention and Treatment of Pre-Eclampsia and Eclampsia (WHO, 2011). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources