Clinical trajectories of individuals with severe mental illness continuing and discontinuing long-acting antipsychotics: a one-year mirror-image analysis from the STAR Network Depot study
- PMID: 37069242
- PMCID: PMC10110527
- DOI: 10.1038/s41537-023-00342-3
Clinical trajectories of individuals with severe mental illness continuing and discontinuing long-acting antipsychotics: a one-year mirror-image analysis from the STAR Network Depot study
Abstract
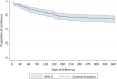
Evidence on long-acting antipsychotics (LAIs) in unselected populations with severe mental illness is scant. In this mirror-image study, we compared multiple clinical outcomes 1 year before and after a first LAI prescription in adults with severe mental illness, describing clinical trajectories of LAI continuers and discontinuers. We compared LAI continuers and discontinuers through Mann-Whitney U test, Kaplan-Meier survival curves, regression for interval-censored data, and a maximum-likelihood mixed-model with individual random-effect and time as predictor. Of the 261 participants analyzed, 71.3% had schizophrenia-spectrum disorders, and 29.5% discontinued the LAI before 1 year. At baseline, LAI discontinuers had a shorter illness duration, lower attitude and adherence scores. The mirror-image analysis showed reduced hospital admissions only for LAI continuers. Over time, continuers spent less days hospitalized, but had more adverse events and more antipsychotics prescribed, with higher overall doses. In conclusion, this study shows that LAIs might be beneficial in unselected patient populations, provided that adherence is maintained. LAI continuers spent less time hospitalized, but received more antipsychotics and suffered from more cumulative adverse events over time. Therefore, the choice of initiating and maintaining a LAI should be carefully weighed on a case-by-case basis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
This research did not receive any funding from commercial or not-for-profit sectors. M.G. has been a consultant and/or a speaker and/or has received research grants from Angelini, Doc Generici, Janssen-Cilag, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Pfizer, Servier, and Recordati. All the other authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative effectiveness of long-acting risperidone in New Zealand: a report of resource utilization and costs in a 12-month mirror-image analysis.Clin Drug Investig. 2010;30(11):777-87. doi: 10.2165/11537680-000000000-00000. Clin Drug Investig. 2010. PMID: 20712387
-
Long-acting injectable versus oral antipsychotics in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of mirror-image studies.J Clin Psychiatry. 2013 Oct;74(10):957-65. doi: 10.4088/JCP.13r08440. J Clin Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 24229745
-
Effect of long-acting injectable antipsychotics on emergency department visits and hospital admissions in people with bipolar disorder: A retrospective mirror-image analysis from the Northern Milan Area Cohort (NOMIAC) study.J Affect Disord. 2022 Dec 1;318:88-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.08.096. Epub 2022 Sep 2. J Affect Disord. 2022. PMID: 36058358
-
Reasons for initiating long-acting antipsychotics in psychiatric practice: findings from the STAR Network Depot Study.Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2020 Dec 22;10:2045125320978102. doi: 10.1177/2045125320978102. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33489087 Free PMC article.
-
Long-acting injectable antipsychotics for the treatment of bipolar disorder: evidence from mirror-image studies.Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2023 Mar 25;13:20451253231163682. doi: 10.1177/20451253231163682. eCollection 2023. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36994116 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Healthcare resource use and costs reduction with aripiprazole once-monthly in schizophrenia: AMBITION, a real-world study.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Aug 4;14:1207307. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1207307. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37599866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kishimoto T, Hagi K, Kurokawa S, Kane JM, Correll CU. Long-acting injectable versus oral antipsychotics for the maintenance treatment of schizophrenia: a systematic review and comparative meta-analysis of randomised, cohort, and pre-post studies. Lancet Psychiatry. 2021;8:387–404. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00039-0. - DOI - PubMed