The bidirectional association between atrial fibrillation and myocardial infarction
- PMID: 37069297
- PMCID: PMC11380523
- DOI: 10.1038/s41569-023-00857-3
The bidirectional association between atrial fibrillation and myocardial infarction
Abstract
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is associated with an increased risk of myocardial infarction (MI) and vice versa. This bidirectional association relies on shared risk factors as well as on several direct and indirect mechanisms, including inflammation, atrial ischaemia, left ventricular remodelling, myocardial oxygen supply-demand mismatch and coronary artery embolism, through which one condition can predispose to the other. Patients with both AF and MI are at greater risk of stroke, heart failure and death than patients with only one of the conditions. In this Review, we describe the bidirectional association between AF and MI. We discuss the pathogenic basis of this bidirectional relationship, describe the risk of adverse outcomes when the two conditions coexist, and review current data and guidelines on the prevention and management of both conditions. We also identify important gaps in the literature and propose directions for future research on the bidirectional association between AF and MI. The Review also features a summary of methodological approaches for the study of bidirectional associations in population-based studies.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
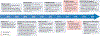
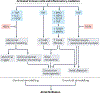

References
-
- Sundbøll J et al. Risk of arterial and venous thromboembolism in patients with atrial fibrillation or flutter: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Int J Cardiol 241, 182–187 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 AG068221/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL141434/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 18SFRN34150007/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- 18SFRN34110082/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

