Syndecan-1 as an immunogene in Triple-negative breast cancer: regulation tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte in the tumor microenviroment and EMT by TGFb1/Smad pathway
- PMID: 37069585
- PMCID: PMC10111802
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-023-02917-7
Syndecan-1 as an immunogene in Triple-negative breast cancer: regulation tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte in the tumor microenviroment and EMT by TGFb1/Smad pathway
Abstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors are the most studied forms of immunotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). The Cancer Genome Map (TCGA) and METABRIC project provide large-scale cancer samples that can be used for comprehensive and reliable immunity-related gene research.
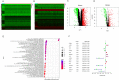
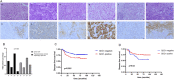
Methods: We analyzed data from TCGA and METABRIC and established an immunity-related gene prognosis model for breast cancer. The SDC1 expression in tumor and cancer associated fibroblasts (CAFs) was then observed in 282 TNBC patients by immunohistochemistry. The effects of SDC1 on MDA-MB-231 proliferation, migration and invasion were evaluated. Qualitative real-time PCR and western blotting were performed to identify mRNA and protein expression, respectively.
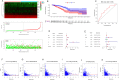
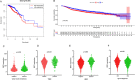
Results: SDC1, as a key immunity-related gene, was significantly correlated with survival in the TCGA and METABRIC databases, while SDC1 was found to be highly expressed in TNBC in the METABRIC database. In the TNBC cohort, patients with high SDC1 expression in tumor cells and low expression in CAFs had significantly lower disease-free survival (DFS) and fewer tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). The downregulation of SDC1 decreased the proliferation of MDA-MB-231, while promoting the migration of MDA-MB-231 cells by reducing the gene expression of E-cadherin and TGFb1 and activating p-Smad2 and p-Smad3 expression.
Conclusion: SDC1 is a key immunity-related gene that is highly expressed TNBC patients. Patients with high SDC1 expression in tumors and low expression in CAFs had poor prognoses and low TILs. Our findings also suggest that SDC1 regulates the migration of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells through a TGFb1-Smad and E-cadherin-dependent mechanism.
Keywords: Prognosis; SDC1; TGFb1-Smad; Triple negative breast cancer; Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor is a key immune-related gene that is correlated with a poor prognosis in patients with triple-negative breast cancer: A bioinformatics analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 18;12:871786. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.871786. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36330486 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Tyrosine Kinase 7 Regulates EGFR/Akt Signaling Pathway and Correlates With Malignant Progression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 22;11:699889. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.699889. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34367983 Free PMC article.
-
Compartmental Syndecan-1 (CD138) expression as a novel prognostic marker in triple-negative metaplastic breast cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Jan;253:154994. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154994. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 38071886
-
Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with triple-negative breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2020 Mar 4;20(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-6668-z. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32131780 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and clinical significance of syndecan-1 expression in breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2019 Jul;45(7):1132-1137. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2018.12.019. Epub 2018 Dec 25. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30598194
Cited by
-
Neutrophil-centric analysis of gastric cancer: prognostic modeling and molecular insights.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Nov 14;81(1):452. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05484-w. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39540948 Free PMC article.
-
Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Progression and Drug Resistance in the Context of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jan 12;17(2):228. doi: 10.3390/cancers17020228. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-omics analyses of the heterogenous immune microenvironment in triple-negative breast cancer implicate UQCRFS1 potentiates tumor progression.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2025 Jun 16;14(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s40164-025-00672-1. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40524231 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive investigation of proteoglycan gene expression in breast cancer: Discovery of a unique proteoglycan gene signature linked to the malignant phenotype.Proteoglycan Res. 2025 Jan-Mar;3(1):e70014. doi: 10.1002/pgr2.70014. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Proteoglycan Res. 2025. PMID: 40066261 Free PMC article.
-
DERL3 facilitates the progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition via regulation of the TGFB1 pathway.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 29;20(4):e0322172. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322172. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40299934 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, et al. Strategies for subtypes–dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol. 2011;22(8):1736–47. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdr304. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

