Seasonal effects decouple SARS-CoV-2 haplotypes worldwide
- PMID: 37069849
- PMCID: PMC10105261
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.131522.1
Seasonal effects decouple SARS-CoV-2 haplotypes worldwide
Abstract
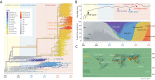
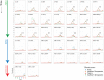
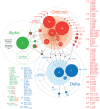
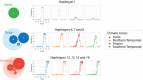
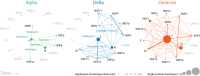
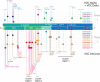
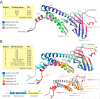
Background: Variants of concern (VOCs) have been replacing each other during the still rampant COVID-19 pandemic. As a result, SARS-CoV-2 populations have evolved increasingly intricate constellations of mutations that often enhance transmissibility, disease severity, and other epidemiological characteristics. The origin and evolution of these constellations remain puzzling. Methods: Here we study the evolution of VOCs at the proteome level by analyzing about 12 million genomic sequences retrieved from GISAID on July 23, 2022. A total 183,276 mutations were identified and filtered with a relevancy heuristic. The prevalence of haplotypes and free-standing mutations was then tracked monthly in various latitude corridors of the world. Results: A chronology of 22 haplotypes defined three phases driven by protein flexibility-rigidity, environmental sensing, and immune escape. A network of haplotypes illustrated the recruitment and coalescence of mutations into major VOC constellations and seasonal effects of decoupling and loss. Protein interaction networks mediated by haplotypes predicted communications impacting the structure and function of proteins, showing the increasingly central role of molecular interactions involving the spike (S), nucleocapsid (N), and membrane (M) proteins. Haplotype markers either affected fusogenic regions while spreading along the sequence of the S-protein or clustered around binding domains. Modeling of protein structure with AlphaFold2 showed that VOC Omicron and one of its haplotypes were major contributors to the distortion of the M-protein endodomain, which behaves as a receptor of other structural proteins during virion assembly. Remarkably, VOC constellations acted cooperatively to balance the more extreme effects of individual haplotypes. Conclusions: Our study uncovers seasonal patterns of emergence and diversification occurring amid a highly dynamic evolutionary landscape of bursts and waves. The mapping of genetically-linked mutations to structures that sense environmental change with powerful ab initio modeling tools demonstrates the potential of deep-learning for COVID-19 predictive intelligence and therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: AlphaFold2; epidemic calendar; membrane protein; mutation; protein interaction; protein structural prediction; proteome; seasonality; spike protein.
Copyright: © 2023 Tomaszewski T et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures



Similar articles
-
AlphaFold2 Reveals Structural Patterns of Seasonal Haplotype Diversification in SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Variants.Biology (Basel). 2024 Feb 21;13(3):134. doi: 10.3390/biology13030134. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38534404 Free PMC article.
-
AlphaFold2 Reveals Structural Patterns of Seasonal Haplotype Diversification in SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Variants.Viruses. 2024 Aug 25;16(9):1358. doi: 10.3390/v16091358. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39339835 Free PMC article.
-
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in Australia by haplotype coalescence reveals a continental link to COVID-19 seasonality.Methods Microbiol. 2022;50:233-268. doi: 10.1016/bs.mim.2022.03.003. Epub 2022 May 17. Methods Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 38013929 Free PMC article.
-
Novel SARS-CoV-2 variants: the pandemics within the pandemic.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021 Aug;27(8):1109-1117. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.022. Epub 2021 May 17. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021. PMID: 34015535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Plasticity and Immune Evasion of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Variants.Viruses. 2022 Jun 9;14(6):1255. doi: 10.3390/v14061255. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35746726 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Virological Characteristics of Five SARS-CoV-2 Variants, Including Beta, Delta and Omicron BA.1, BA.2, BA.5.Viruses. 2023 Dec 8;15(12):2394. doi: 10.3390/v15122394. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38140635 Free PMC article.
-
On Protein Loops, Prior Molecular States and Common Ancestors of Life.J Mol Evol. 2024 Oct;92(5):624-646. doi: 10.1007/s00239-024-10167-y. Epub 2024 Apr 23. J Mol Evol. 2024. PMID: 38652291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AlphaFold2 Reveals Structural Patterns of Seasonal Haplotype Diversification in SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Variants.Biology (Basel). 2024 Feb 21;13(3):134. doi: 10.3390/biology13030134. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38534404 Free PMC article.
-
Haplotypic Distribution of SARS-CoV-2 Variants in Cases of Intradomiciliary Infection in the State of Rondônia, Western Amazon.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2024 Nov 21;18:11779322241266354. doi: 10.1177/11779322241266354. eCollection 2024. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2024. PMID: 39574519 Free PMC article.
-
AlphaFold2 Reveals Structural Patterns of Seasonal Haplotype Diversification in SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Variants.Viruses. 2024 Aug 25;16(9):1358. doi: 10.3390/v16091358. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39339835 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

