Identification of Glomerular and Plasma Apolipoprotein M as Novel Biomarkers in Glomerular Disease
- PMID: 37069998
- PMCID: PMC10105063
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2023.01.031
Identification of Glomerular and Plasma Apolipoprotein M as Novel Biomarkers in Glomerular Disease
Abstract
Introduction: Dysregulation of sphingolipid and cholesterol metabolism contributes to the pathogenesis of glomerular diseases (GDs). Apolipoprotein M (ApoM) promotes cholesterol efflux and modulates the bioactive sphingolipid sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P). Glomerular ApoM expression is decreased in patients with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). We hypothesized that glomerular ApoM deficiency occurs in GD and that ApoM expression and plasma ApoM correlate with outcomes.
Methods: Patients with GD from the Nephrotic Syndrome Study Network (NEPTUNE) were studied. We compared glomerular mRNA expression of ApoM (gApoM), sphingosine kinase 1 (SPHK1), and S1P receptors 1 to 5 (S1PR1-5) in patients (n = 84) and controls (n = 6). We used correlation analyses to determine associations between gApoM, baseline plasma ApoM (pApoM), and urine ApoM (uApoM/Cr). We used linear regression to determine whether gApoM, pApoM, and uApoM/Cr were associated with baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and proteinuria. Using Cox models, we determined whether gApoM, pApoM, and uApoM/Cr were associated with complete remission (CR) and the composite of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) or ≥40% eGFR decline.
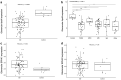
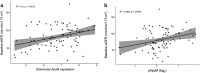
Results: gApoM was reduced (P < 0.01) and SPHK1 and S1PR1 to 5 expression was increased (P < 0.05) in patients versus controls, consistent with ApoM/S1P pathway modulation. gApoM positively correlated with pApoM in the overall cohort (r = 0.34, P < 0.01) and in the FSGS (r = 0.48, P < 0.05) and minimal change disease (MCD) (r = 0.75, P < 0.05) subgroups. Every unit decrease in gApoM and pApoM (log2) was associated with a 9.77 ml/min per 1.73 m2 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 3.96-15.57) and 13.26 ml/min per 1.73 m2 (95% CI: 3.57-22.96) lower baseline eGFR, respectively (P < 0.01). From Cox models adjusted for age, sex, or race, pApoM was a significant predictor of CR (hazard ratio [HR]: 1.85; 95% CI: 1.06-3.23).
Conclusions: pApoM is a potential noninvasive biomarker of gApoM deficiency and strongly associates with clinical outcomes in GD.
Keywords: apolipoprotein M; biomarkers; glomerular disease; nephrotic syndrome; outcome prediction.
© 2023 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Quantification of Glomerular Structural Lesions: Associations With Clinical Outcomes and Transcriptomic Profiles in Nephrotic Syndrome.Am J Kidney Dis. 2022 Jun;79(6):807-819.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.10.004. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Am J Kidney Dis. 2022. PMID: 34864148 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate and its carrier apolipoprotein M in human sepsis and in Escherichia coli sepsis in baboons.J Cell Mol Med. 2016 Jun;20(6):1170-81. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12831. Epub 2016 Mar 17. J Cell Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 26990127 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma levels of sphingosine-1-phosphate and apolipoprotein M in patients with monogenic disorders of HDL metabolism.Atherosclerosis. 2011 Dec;219(2):855-63. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.08.049. Epub 2011 Sep 6. Atherosclerosis. 2011. PMID: 21944699
-
Apolipoprotein M and its impact on endothelial dysfunction and inflammation in the cardiovascular system.Atherosclerosis. 2021 Oct;334:76-84. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2021.08.039. Epub 2021 Aug 27. Atherosclerosis. 2021. PMID: 34482091 Review.
-
The apoM/S1P Complex-A Mediator in Kidney Biology and Disease?Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Oct 14;8:754490. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.754490. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34722589 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Normal and Dysregulated Sphingolipid Metabolism: Contributions to Podocyte Injury and Beyond.Cells. 2024 May 22;13(11):890. doi: 10.3390/cells13110890. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38891023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingolipids and Chronic Kidney Disease.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 26;13(17):5050. doi: 10.3390/jcm13175050. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39274263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kidney lipid dysmetabolism and lipid droplet accumulation in chronic kidney disease.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2023 Oct;19(10):629-645. doi: 10.1038/s41581-023-00741-w. Epub 2023 Jul 27. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37500941 Review.
-
Apolipoprotein M gene polymorphisms in childhood-onset type 1 diabetes in southern Brazil.Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 2023 Aug 15;14(4):51-61. eCollection 2023. Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37736389 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

