Extracellular vesicles as markers and mediators of pregnancy complications: gestational diabetes, pre-eclampsia, preterm birth and fetal growth restriction
- PMID: 37070801
- PMCID: PMC11497252
- DOI: 10.1113/JP282849
Extracellular vesicles as markers and mediators of pregnancy complications: gestational diabetes, pre-eclampsia, preterm birth and fetal growth restriction
Abstract
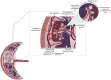
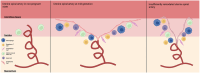
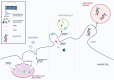
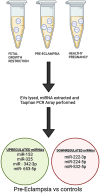
In high income countries, approximately 10% of pregnancies are complicated by pre-eclampsia (PE), preterm birth (PTB), fetal growth restriction (FGR) and/or macrosomia resulting from gestational diabetes (GDM). Despite the burden of disease this places on pregnant people and their newborns, there are still few, if any, effective ways of preventing or treating these conditions. There are also gaps in our understanding of the underlying pathophysiologies and our ability to predict which mothers will be affected. The placenta plays a crucial role in pregnancy, and alterations in placental structure and function have been implicated in all of these conditions. As extracellular vesicles (EVs) have emerged as important molecules in cell-to-cell communication in health and disease, recent research involving maternal- and placental-derived EV has demonstrated their potential as predictive and diagnostic biomarkers of obstetric disorders. This review will consider how placental and maternal EVs have been investigated in pregnancies complicated by PE, PTB, FGR and GDM and aims to highlight areas where further research is required to enhance the management and eventual treatment of these pathologies.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles; fetal growth restriction; gestational diabetes; placenta; pre-eclampsia; pre-term birth.
© 2023 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests declared
Figures

References
-
- Alshabibi, M. A. , Khatlani, T. , Abomaray, F. M. , AlAskar, A. S. , Kalionis, B. , Messaoudi, S. A. , Khanabdali, R. , Alawad, A. O. , & Abumaree, M. H. (2018). Human decidua basalis mesenchymal stem/stromal cells protect endothelial cell functions from oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide and monocytes. Stem Cell Research and Therapy, 9(1), 275. - PMC - PubMed
-
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (2020). Gestational hypertension and preeclampsia: ACOG Practice Bulletin Summary, Number 222. Obstetrics and Gynecology, 135(6), 1492–1495. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

