The N-terminal disordered region of ChsB regulates its efficient transport to the hyphal apical surface in Aspergillus nidulans
- PMID: 37071151
- PMCID: PMC10163080
- DOI: 10.1007/s00294-023-01267-1
The N-terminal disordered region of ChsB regulates its efficient transport to the hyphal apical surface in Aspergillus nidulans
Abstract
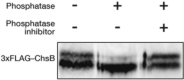
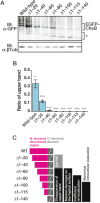
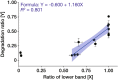
In fungi, the cell wall plays a crucial role in morphogenesis and response to stress from the external environment. Chitin is one of the main cell wall components in many filamentous fungi. In Aspergillus nidulans, a class III chitin synthase ChsB plays a pivotal role in hyphal extension and morphogenesis. However, little is known about post-translational modifications of ChsB and their functional impacts. In this study, we showed that ChsB is phosphorylated in vivo. We characterized strains that produce ChsB using stepwise truncations of its N-terminal disordered region or deletions of some residues in that region and demonstrated its involvement in ChsB abundance on the hyphal apical surface and in hyphal tip localization. Furthermore, we showed that some deletions in this region affected the phosphorylation states of ChsB, raising the possibility that these states are important for the localization of ChsB to the hyphal surface and the growth of A. nidulans. Our findings indicate that ChsB transport is regulated by its N-terminal disordered region.
Keywords: Aspergillus nidulans; Chitin synthase; ChsB; Intrinsically disordered region; Phosphorylation.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transportation of Aspergillus nidulans Class III and V Chitin Synthases to the Hyphal Tips Depends on Conventional Kinesin.PLoS One. 2015 May 8;10(5):e0125937. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125937. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25955346 Free PMC article.
-
AP-2 complex contributes to hyphal-tip-localization of a chitin synthase in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans.Fungal Biol. 2021 Oct;125(10):806-814. doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2021.05.009. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Fungal Biol. 2021. PMID: 34537176
-
The chsB gene of Aspergillus nidulans is necessary for normal hyphal growth and development.Fungal Genet Biol. 1996 Sep;20(3):193-203. doi: 10.1006/fgbi.1996.0035. Fungal Genet Biol. 1996. PMID: 8953267
-
Control of Actin and Calcium for Chitin Synthase Delivery to the Hyphal Tip of Aspergillus.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2020;425:113-129. doi: 10.1007/82_2019_193. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31974757 Review.
-
Functional diversity of chitin synthases of Aspergillus nidulans in hyphal growth, conidiophore development and septum formation.Med Mycol. 2009;47 Suppl 1:S47-52. doi: 10.1080/13693780802213332. Epub 2008 Jul 14. Med Mycol. 2009. PMID: 18651309 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

