Four-factor risk score for the prediction of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 37071179
- PMCID: PMC10261234
- DOI: 10.1007/s00296-023-05313-6
Four-factor risk score for the prediction of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is one of the commonest systemic complications in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and carries a significant morbidity and mortality burden. We aimed to identify key variables to risk-stratify RA patients in order to identify those at increased risk of developing ILD. We propose a probability score based on the identification of these variables.
Methods: A retrospective, multicentre study using clinical data collected between 2010 and 2020, across 20 centres.
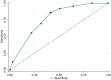
Results: A total of 430 RA (210 with ILD confirmed on high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT)) patients were evaluated. We explored several independent variables for the risk of developing ILD in RA and found that the key significant variables were smoking (past or present), older age and positive rheumatoid factor/anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide. Multivariate logistic regression models were used to form a scoring system for categorising patients into high and low risk on a scale of 0-9 points and a cut-off score of 5, based on the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.76 (CI 95% 0.71-0.82). This yielded a sensitivity of 86% and a specificity of 58%. High-risk patients should be considered for investigation with HRCT and monitored closely.
Conclusion: We have proposed a new model for identifying RA patients at risk of developing ILD. This approach identified four simple clinical variables: age, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies, Rheumatoid factor and smoking, which allowed development of a predictive scoring system for the presence of ILD in patients with RA.
Keywords: Extra-articular manifestation; Interstitial lung disease; Probability score; Rheumatoid arthritis; Risk prediction.
© 2023. Crown.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High-resolution computed tomography of the lung in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Prevalence of interstitial lung disease involvement and determinants of abnormalities.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Sep;98(38):e17088. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017088. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31567944 Free PMC article.
-
Rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: associations, prognostic factors and physiological and radiological characteristics--a large multicentre UK study.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014 Sep;53(9):1676-82. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keu165. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014. PMID: 24758887
-
Clinical characteristics associated with occurrence and poor prognosis of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis.Korean J Intern Med. 2019 Mar;34(2):434-441. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2016.349. Epub 2017 Mar 28. Korean J Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 28352064 Free PMC article.
-
Etiology and Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis-Interstitial Lung Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 25;24(19):14509. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914509. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37833957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The multifaceted aspects of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:759760. doi: 10.1155/2013/759760. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24205507 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Meta-analysis identifies the major impact of patient classification on the ACPA association with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD).Arthritis Res Ther. 2025 Jul 19;27(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s13075-025-03617-5. Arthritis Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40684237 Free PMC article.
-
A Practical Multidisciplinary Approach to Identifying Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases: A Clinician's Narrative Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Nov 27;14(23):2674. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14232674. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and validation of predictive factors influencing rheumatoid arthritis associated with interstitial lung disease.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Feb;44(2):601-613. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07282-y. Epub 2024 Dec 26. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39724289
-
Risk factors for interstitial lung disease in early rheumatoid arthritis and external validation of screening strategies: Baseline results of SAIL-RA.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 27:2025.01.24.25321091. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.24.25321091. medRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39974108 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Rheumatoid Factor: Diagnostic and Prognostic Performance and Therapeutic Implications in Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 25;14(5):1529. doi: 10.3390/jcm14051529. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40094988 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous