The HDAC inhibitor domatinostat induces type I interferon α in Merkel cell carcinoma by HES1 repression
- PMID: 37071208
- PMCID: PMC10374800
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-023-04733-y
The HDAC inhibitor domatinostat induces type I interferon α in Merkel cell carcinoma by HES1 repression
Abstract
Background: Class I selective histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) have been previously demonstrated to not only increase major histocompatibility complex class I surface expression in Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) cells by restoring the antigen processing and presentation machinery, but also exert anti-tumoral effect by inducing apoptosis. Both phenomena could be due to induction of type I interferons (IFN), as has been described for HDACi. However, the mechanism of IFN induction under HDACi is not fully understood because the expression of IFNs is regulated by both activating and inhibitory signaling pathways. Our own preliminary observations suggest that this may be caused by suppression of HES1.
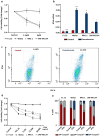
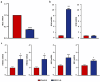
Methods: The effect of the class I selective HDACi domatinostat and IFNα on cell viability and the apoptosis of MCPyV-positive (WaGa, MKL-1) and -negative (UM-MCC 34) MCC cell lines, as well as, primary fibroblasts were assessed by colorimetric methods or measuring mitochondrial membrane potential and intracellular caspase-3/7, respectively. Next, the impact of domatinostat on IFNA and HES1 mRNA expression was measured by RT-qPCR; intracellular IFNα production was detected by flow cytometry. To confirm that the expression of IFNα induced by HDACi was due to the suppression of HES1, it was silenced by RNA interference and then mRNA expression of IFNA and IFN-stimulated genes was assessed.
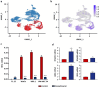
Results: Our studies show that the previously reported reduction in viability of MCC cell lines after inhibition of HDAC by domatinostat is accompanied by an increase in IFNα expression, both of mRNA and at the protein level. We confirmed that treatment of MCC cells with external IFNα inhibited their proliferation and induced apoptosis. Re-analysis of existing single-cell RNA sequencing data indicated that induction of IFNα by domatinostat occurs through repression of HES1, a transcriptional inhibitor of IFNA; this was confirmed by RT-qPCR. Finally, siRNA-mediated silencing of HES1 in the MCC cell line WaGa not only increased mRNA expression of IFNA and IFN-stimulated genes but also decreased cell viability.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that the direct anti-tumor effect of HDACi domatinostat on MCC cells is at least in part mediated via decreased HES1 expression allowing the induction of IFNα, which in turn causes apoptosis.
Keywords: HES1; Histone deacetylase inhibitor; Interferon-stimulated genes; Interferons; Merkel cell carcinoma.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
T.G. has received speakers and/or advisory board honoraria from BMS, Sanofi Genzyme, MSD, Novartis Pharma, Roche, Abbvie, Almirall, Janssen, Lilly, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Merck Serono, outside the submitted work. J.C.B. is receiving speaker’s bureau honoraria from Almirall, Amgen, Pfizer, Merck Serono, Recordati and Sanofi, and is a paid consultant/advisory board member for Merck Serono, Pfizer, 4SC, Recordati, InProTher, and Sanofi. His group receives research grants from Merck Serono, IQVIA and Alcedis GmbH. None of the other authors indicated any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Sun protection for preventing basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jul 25;7(7):CD011161. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011161.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27455163 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the landscape of non-melanoma skin cancer through single-cell RNA sequencing technology.Front Oncol. 2024 Nov 4;14:1500300. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1500300. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39558960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted intervention of tumor microenvironment with HDAC inhibitors and their combination therapy strategies.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Feb 4;30(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02326-8. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 39905506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hiding in Plain Sight: An Atypical Presentation of the Uncommon Merkel Cell Carcinoma.Cureus. 2024 Mar 6;16(3):e55613. doi: 10.7759/cureus.55613. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38586682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cenciarelli C, Marei HE, Zonfrillo M, Casalbore P, Felsani A, Giannetti S, Trevisi G, Althani A, Mangiola A (2017) The interference of Notch1 target Hes1 affects cell growth, differentiation and invasiveness of glioblastoma stem cells through modulation of multiple oncogenic targets. Oncotarget 8:17873–17886 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen K, Liu J, Cao X (2017) Regulation of type I interferon signaling in immunity and inflammation: a comprehensive review. J Autoimmun 83:1–11 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

