Colloidal inorganic nano- and microparticles for passive daytime radiative cooling
- PMID: 37071232
- PMCID: PMC10113424
- DOI: 10.1186/s40580-023-00365-7
Colloidal inorganic nano- and microparticles for passive daytime radiative cooling
Abstract
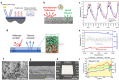
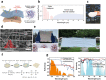
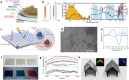
Compared to traditional cooling systems, radiative cooling (RC) is a promising cooling strategy in terms of reducing energy consumption enormously and avoiding severe environmental issues. Radiative cooling materials (RCMs) reduce the temperature of objects without using an external energy supply by dissipating thermal energy via infrared (IR) radiation into the cold outer space through the atmospheric window. Therefore, RC has a great potential for various applications, such as energy-saving buildings, vehicles, water harvesting, solar cells, and personal thermal management. Herein, we review the recent progress in the applications of inorganic nanoparticles (NPs) and microparticles (MPs) as RCMs and provide insights for further development of RC technology. Particle-based RCMs have tremendous potential owing to the ease of engineering their optical and physical properties, as well as processibility for facile, inexpensive, and large area deposition. The optical and physical properties of inorganic NPs and MPs can be tuned easily by changing their size, shape, composition, and crystals structures. This feature allows particle-based RCMs to fulfill requirements pertaining to passive daytime radiative cooling (PDRC), which requires high reflectivity in the solar spectrum and high emissivity within the atmospheric window. By adjusting the structures and compositions of colloidal inorganic particles, they can be utilized to design a thermal radiator with a selective emission spectrum at wavelengths of 8-13 μm, which is preferable for PDRC. In addition, colloidal particles can exhibit high reflectivity in the solar spectrum through Mie-scattering, which can be further engineered by modifying the compositions and structures of colloidal particles. Recent advances in PDRC that utilize inorganic NPs and MPs are summarized and discussed together with various materials, structural designs, and optical properties. Subsequently, we discuss the integration of functional NPs to achieve functional RCMs. We describe various approaches to the design of colored RCMs including structural colors, plasmonics, and luminescent wavelength conversion. In addition, we further describe experimental approaches to realize self-adaptive RC by incorporating phase-change materials and to fabricate multifunctional RC devices by using a combination of functional NPs and MPs.
Keywords: Colloid; Microparticle; Multifunctionality; Nanoparticle; Radiative cooling; Thermal management.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Cook BI, Smerdon JE, Seager R, Coats S. Clim. Dyn. 2014;43(9):2607–2627. doi: 10.1007/s00382-014-2075-y. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
