Antibody drug conjugates as targeted cancer therapy: past development, present challenges and future opportunities
- PMID: 37071273
- PMCID: PMC11345756
- DOI: 10.1007/s12272-023-01447-0
Antibody drug conjugates as targeted cancer therapy: past development, present challenges and future opportunities
Erratum in
-
Correction: Antibody drug conjugates as targeted cancer therapy: past development, present challenges and future opportunities.Arch Pharm Res. 2024 Jul;47(7):675. doi: 10.1007/s12272-024-01502-4. Arch Pharm Res. 2024. PMID: 38926231 No abstract available.
Abstract
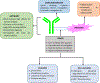
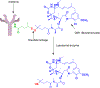
Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) are promising cancer therapeutics with minimal toxicity as compared to small cytotoxic molecules alone and have shown the evidence to overcome resistance against tumor and prevent relapse of cancer. The ADC has a potential to change the paradigm of cancer chemotherapeutic treatment. At present, 13 ADCs have been approved by USFDA for the treatment of various types of solid tumor and haematological malignancies. This review covers the three structural components of an ADC-antibody, linker, and cytotoxic payload-along with their respective structure, chemistry, mechanism of action, and influence on the activity of ADCs. It covers comprehensive insight on structural role of linker towards efficacy, stability & toxicity of ADCs, different types of linkers & various conjugation techniques. A brief overview of various analytical techniques used for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of ADC is summarized. The current challenges of ADCs, such as heterogeneity, bystander effect, protein aggregation, inefficient internalization or poor penetration into tumor cells, narrow therapeutic index, emergence of resistance, etc., are outlined along with recent advances and future opportunities for the development of more promising next-generation ADCs.
Keywords: ADC; Cancer treatment; DAR; Linkers; Site specific conjugation; Targeted therapy.
© 2023. The Pharmaceutical Society of Korea.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


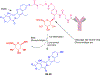
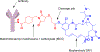

References
-
- Abdollahpour-Alitappeh M, Lotfinia M, Gharibi T, Mardaneh J, Farhadihosseinabadi B, Larki P, Faghfourian B, Sepehr KS, Abbaszadeh-Goudarzi K, Abbaszadeh-Goudarzi G, Johari B, Zali MR, Bagheri N (2019) Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) for cancer therapy: strategies, challenges, and successes. J Cell Physiol 234:5628–5642. 10.1002/jcp.27419 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ackerman S, Pearson C, Gregorio J, Gonzalez J, Kenkel J, Hartmann F, Luo A, Ho P, LeBlanc H, Blum L, Kimmey S, Luo A, Nguyen M, Paik J, Sheu L, Ackerman B, Lee A, Li H, Melrose J, Laura R, Ramani V, Henning K, Jackson D, Safina B, Yonehiro G, Devens B, Carmi Y, Chapin S, Bendall S, Kowanetz M, Dornan D, Engleman E, Alonso M (2021) Immune-stimulating antibody conjugates elicit robust myeloid activation and durable antitumor immunity. Nat Cancer 2:18–33. 10.1038/s43018-020-00136-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

