Seroprevalence of Lyme Borreliosis in Europe: Results from a Systematic Literature Review (2005-2020)
- PMID: 37071401
- PMCID: PMC10122246
- DOI: 10.1089/vbz.2022.0069
Seroprevalence of Lyme Borreliosis in Europe: Results from a Systematic Literature Review (2005-2020)
Abstract
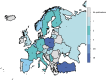
Background: Lyme borreliosis (LB), a tick bite-transmitted infection caused by Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato (Bbsl) complex spirochetes, is the most common tickborne disease in Europe. Studies in European countries have reported LB seroprevalence (prevalence of antibodies to Bbsl infection) and diagnostic strategies used for testing. We conducted a systematic literature review to summarize contemporary LB seroprevalence in Europe. Methods: PubMed, Embase, and CABI Direct (Global Health) databases were searched from 2005 to 2020 to identify studies reporting LB seroprevalence in European countries. Reported single-tier and two-tier test results were summarized; algorithms (standard or modified) were used to interpret final test results from studies that used two-tier testing. Results: The search yielded 61 articles from 22 European countries. Studies used a range of diagnostic testing methods and strategies (48% single-tier, 46% standard two-tier, and 6% modified two-tier). In 39 population-based studies, of which 14 were nationally representative, seroprevalence estimates ranged from 2.7% (Norway) to 20% (Finland). There was substantial heterogeneity among studies in terms of design, cohort types, periods sampled, sample sizes, and diagnostics, which limited cross-study comparisons. Nevertheless, among studies that reported seroprevalence in persons with greater exposure to ticks, LB seroprevalence was higher among these groups than in the general population (40.6% vs. 3.9%). Furthermore, among studies that used two-tier testing, general population LB seroprevalence was higher in Western Europe (13.6%) and Eastern Europe (11.1%) than in Northern Europe (4.2%) and Southern Europe (3.9%). Conclusion: Despite variations in LB seroprevalence between and within European subregions and countries, high seroprevalence was observed in certain geographic regions and particular risk groups, suggesting significant disease burden and supporting the need for improved, targeted public health interventions such as vaccination. Harmonized approaches to serologic testing and more nationally representative seroprevalence studies are needed to better understand the prevalence of Bbsl infection in Europe.
Keywords: Europe; Lyme borreliosis; diagnostics; epidemiology; seropositivity; seroprevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
J.H.S., F.J.A., B.D.G., A.P., A.V., M.A.F., and J.C.M. are all employees of Pfizer and may hold stock options or stock in Pfizer. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aslan Başbulut E, Gözalan A, Sönmez C, Çöplü N, et al. [Seroprevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi and tick-borne encephalitis virus in a rural area of Samsun, Turkey]. Mikrobiyol Bul 2012; 46:247–256. - PubMed
-
- Barreiro-Hurle L, Melon-Garcia S, Seco-Bernal C, Munoz-Turrillas C, et al. . Seroprevalence of Lyme disease in southwest Asturias. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin 2020; 38:155–158. - PubMed
-
- Bazovská S, Guryčová D, Výrosteková V, Jareková J, et al. . [Antibodies against the causative agents of some natural focal infections in blood donor sera from western Slovakia]. Epidemiol Mikrobiol Immunol 2010; 59:168–171.
-
- Bazovska S, Machacova E, Spalekova M, Kontrosova S. Reported incidence of Lyme disease in Slovakia and antibodies to B. burgdorferi antigens detected in healthy population. Bratisl Lek Listy 2005; 106:270–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
