MicroRNA expression in extracellular vesicles as a novel blood-based biomarker for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 37071449
- PMCID: PMC11663460
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.13055
MicroRNA expression in extracellular vesicles as a novel blood-based biomarker for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Introduction: Brain cell-derived small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) in blood offer unique cellular and molecular information related to the onset and progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD). We simultaneously enriched six specific sEV subtypes from the plasma and analyzed a selected panel of microRNAs (miRNAs) in older adults with/without cognitive impairment.
Methods: Total sEVs were isolated from the plasma of participants with normal cognition (CN; n = 11), mild cognitive impairment (MCI; n = 11), MCI conversion to AD dementia (MCI-AD; n = 6), and AD dementia (n = 11). Various brain cell-derived sEVs (from neurons, astrocytes, microglia, oligodendrocytes, pericytes, and endothelial cells) were enriched and analyzed for specific miRNAs.
Results: miRNAs in sEV subtypes differentially expressed in MCI, MCI-AD, and AD dementia compared to the CN group clearly distinguished dementia status, with an area under the curve (AUC) > 0.90 and correlated with the temporal cortical region thickness on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Discussion: miRNA analyses in specific sEVs could serve as a novel blood-based molecular biomarker for AD.
Highlights: Multiple brain cell-derived small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) could be isolated simultaneously from blood. MicroRNA (miRNA) expression in sEVs could detect Alzheimer's disease (AD) with high specificity and sensitivity. miRNA expression in sEVs correlated with cortical region thickness on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Altered expression of miRNAs in sEVCD31 and sEVPDGFRβ suggested vascular dysfunction. miRNA expression in sEVs could predict the activation state of specific brain cell types.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; biomarker; brain cells; extracellular vesicles; microRNA.
© 2023 The Authors. Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
GD is the founder of LiBiCo, which has no influence or contribution to the work presented in this manuscript. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures

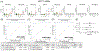
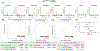
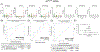


References
-
- Gauthier SR-NP, Morais JA, Webster C, World Alzheimer Report 2021: Journey through the diagnosis of dementia. 2021.
-
- DeStrooper B, Karran E. The cellular phase of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell. 2016;164(4):603–615. - PubMed
-
- Dzamba D, Harantova L, Butenko O, Anderova M. Glial cells - The key elements of Alzheimer s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13(8):894–911. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

