Comprehensive Interactome Mapping of the DNA Repair Scaffold SLX4 Using Proximity Labeling and Affinity Purification
- PMID: 37071664
- PMCID: PMC10243116
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.2c00706
Comprehensive Interactome Mapping of the DNA Repair Scaffold SLX4 Using Proximity Labeling and Affinity Purification
Abstract
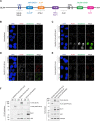
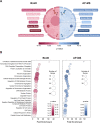
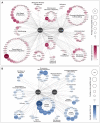
The DNA repair scaffold SLX4 has pivotal roles in cellular processes that maintain genome stability, most notably homologous recombination. Germline mutations in SLX4 are associated with Fanconi anemia, a disease characterized by chromosome instability and cancer susceptibility. The role of mammalian SLX4 in homologous recombination depends critically on binding and activating structure-selective endonucleases, namely SLX1, MUS81-EME1, and XPF-ERCC1. Increasing evidence indicates that cells rely on distinct SLX4-dependent complexes to remove DNA lesions in specific regions of the genome. Despite our understanding of SLX4 as a scaffold for DNA repair proteins, a detailed repertoire of SLX4 interactors has never been reported. Here, we provide a comprehensive map of the human SLX4 interactome using proximity-dependent biotin identification (BioID) and affinity purification coupled to mass spectrometry (AP-MS). We identified 221 unique high-confidence interactors, of which the vast majority represent novel SLX4-binding proteins. Network analysis of these hits revealed pathways with known involvement of SLX4, such as DNA repair, and several emerging pathways of interest, including RNA metabolism and chromatin remodeling. In summary, the comprehensive SLX4 interactome we report here provides a deeper understanding of how SLX4 functions in DNA repair while revealing new cellular processes that may involve SLX4.
Keywords: AP-MS; BioID; DNA repair; SLX4; genome stability; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Human SLX4 is a Holliday junction resolvase subunit that binds multiple DNA repair/recombination endonucleases.Cell. 2009 Jul 10;138(1):78-89. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.06.029. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19596236 Free PMC article.
-
SLX4: multitasking to maintain genome stability.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2018 Oct;53(5):475-514. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2018.1488803. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30284473 Review.
-
Coordination of structure-specific nucleases by human SLX4/BTBD12 is required for DNA repair.Mol Cell. 2009 Jul 10;35(1):116-27. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.06.020. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19595721
-
Phosphorylation of the DNA repair scaffold SLX4 drives folding of the SAP domain and activation of the MUS81-EME1 endonuclease.Cell Rep. 2022 Oct 25;41(4):111537. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111537. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 36288699
-
Coordinated roles of SLX4 and MutSβ in DNA repair and the maintenance of genome stability.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2021 Apr;56(2):157-177. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2021.1881433. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33596761 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiplexed in vivo base editing identifies functional gene-variant-context interactions.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 26:2025.02.23.639770. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.23.639770. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40060482 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Mapping protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2024 May 14:10.1002/mas.21887. doi: 10.1002/mas.21887. Online ahead of print. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2024. PMID: 38742660 Review.
-
Engineered Proteins and Chemical Tools to Probe the Cell Surface Proteome.Chem Rev. 2025 Apr 23;125(8):4069-4110. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00554. Epub 2025 Apr 3. Chem Rev. 2025. PMID: 40178992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Mass Spectrometry-Based Protein Interactome Studies.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2025 Jan;24(1):100887. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2024.100887. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2025. PMID: 39608603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The BLM-TOP3A-RMI1-RMI2 proximity map reveals that RAD54L2 suppresses sister chromatid exchanges.EMBO Rep. 2025 Mar;26(5):1290-1314. doi: 10.1038/s44319-025-00374-z. Epub 2025 Jan 27. EMBO Rep. 2025. PMID: 39870965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takata M.; Sasaki M. S.; Sonoda E.; Morrison C.; Hashimoto M.; Utsumi H.; Yamaguchi-Iwai Y.; Shinohara A.; Takeda S. Homologous recombination and non-homologous end-joining pathways of DNA double-strand break repair have overlapping roles in the maintenance of chromosomal integrity in vertebrate cells. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 5497–5508. 10.1093/emboj/17.18.5497. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

